Synergistic effects of Ti\(_{3}\)C\(_{2}\)T\(_{x}\) MXene on the structural and dielectric properties of blend-based dielectrics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v35i1.2274Keywords:
2D composite, MXene, Dielectrics, Structural, MorphologyAbstract
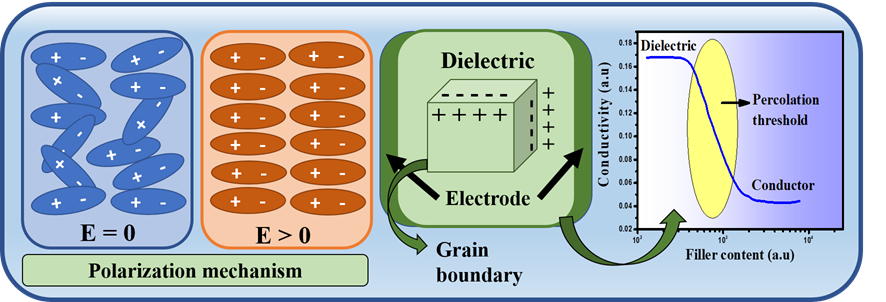
The PVDF/PMMA-Ti₃C₂Tx MXene composite (PMC) films are processed via the solution casting method. The various phases (α, β) of PVDF have been identified through analysis using an X-ray diffractometer and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy instruments. The maximum percentage β phase (%) obtained was 73.15%, which corresponds to a 10.0 wt% composite film. The structural analysis revealed that the Ti3C2Tx nanoparticles are immiscibly distributed throughout the blend matrix, allowing the electrical conductivity and dielectric constant values to noticeably increase at constant frequency. The highest dielectric loss of 0.077 and the highest dielectric constant (εr) of 191.5 (at 100 Hz) were observed in the nanocomposites (NCs) film having 20 wt% Ti3C2Tx MXene. The relative permittivity rises with increasing filler content because of high electrostatics and the interfacial polarization between the neat blend (‒CH2‒CF2 dipole) and filler. The percolation behavior is displayed by the conducting composite, and the percolation threshold has been shown to be more than 20 wt% MXene. The present study offers a novel perspective on the enhanced structural and dielectric properties of the composite system.
Downloads
References
N. K. Nath, R. R. Mohanta, R. K. Parida, B. N. Parida, and N. C. Nayak, “Improving the energy storage efficiency and power density of polymer blend in combination with Ti3C2Tx for energy storage devices,” Materials Today Chemistry, vol. 41, p. 102338, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2024.102338
V. O. C. Concha, L. Timoteo, L. A. N. Duarte, J. O. Bahu, F. Lopez, A. P. Silva, L. Lodi, P. Severino, J. I. Pulido, and E. B. Souto, “Properties, characterization and biomedical applications of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): A review,” Journal of Materials Science, vol. 59, no. 31, pp. 14185-14204, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10046-3
G. H. Kim, S. M. Hong, and Y. Seo, “Piezoelectric properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride) and carbon nanotube blends: β-phase development,” Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, vol. 11, no. 44, p. 10506, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b912801h
V. R. P, D. V. Khakhar, and A. Misra, “Studies on α to β phase transformations in mechanically deformed PVDF films,” Journal of Applied Polymer Science, vol. 117, no. 6, pp. 3491-3497, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.32218
S. He, Q. Zhu, R. A. Soomro, and B. Xu, “MXene derivatives for energy storage applications,” Sustainable Energy & Fuels, vol. 4, no. 10, pp. 4988-5004, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SE00927J
J. A. A. L. Jayarathna, S. Hajra, S. Panda, E. Chamanehpour, I. Sulania, M. S. Goyat, S.-H. Hsu, H. J. Kim, T. Treeratanaphitak, and Y. K. Mishra, “Exploring potential of MXenes in smart sensing and energy harvesting,” Materials Letters, vol. 363, p. 136252, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2024.136252
F.-C. Chiu, and Y.-J. Chen, “Evaluation of thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties of PVDF/GNP binary and PVDF/PMMA/ GNP ternary nanocomposites,” Composites Part a Applied Science and Manufacturing, vol. 68, pp. 62-71, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.09.019
M. P. Niharika, R. Garlapallya, K. Ruthvik, M. Velaga, and B. M. Rao, “Hydrogen production on g-C3N4 nanoflakes via photo-electrochemical water splitting,” Materials Today Proceedings, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.06.188
K. Y. Fang, F. Fang, S. W. Wang, W. Yang, W. Sun, and J. F. Li, “Hybridizing CNT/PMMA/PVDF towards high-performance piezoelectric nanofibers,” Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, vol. 51, no. 26, p. 265305, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aac600
V. Khade, and M. Wuppulluri, “Microwave absorption performance of flexible porous PVDF-MWCNT foam in the X-band frequency range,” ACS Omega, vol. 9, no. 33, pp. 35364-35373, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.4c00995
N. Augustin, P. Muraliharan, A. Sabu, K. K. Senthilkumar, P. K. Annamalai, and R. B. T. S. Raghava, “Unravelling the role of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) molecular weight in poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/PMMA/expanded graphite (ExGr) blend nanocomposites: Insights into morphology, thermal behavior, electrical conductivity, and wetting property,” Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, vol. 37, no. 8, pp. 2527-2570, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/08927057241238203
P. R. Sumbe, U. Chhote, G. Sanyal, B. Chakraborty, A. Sayeed, and M. A. More, “Synthesis, physico-chemical characterization, DFT simulation, and field electron behaviour of 2D layered Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets,” Nano Express, vol. 5, no. 3, p. 035005, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/2632-959X/ad58fd
Y. Li, X. Zhou, J. Wang, Q. Deng, M. Li, S. Du, Y.-H. Han, J. Lee, and Q. Huang, “Facile preparation of in situ coated Ti3C2Tx/Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composites and their electromagnetic performance,” RSC Advances, vol. 7, no. 40, pp. 24698-24708, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA03402D
X. Cai, T. Lei, D. Sun, and L. Lin, “A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly (vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR,” RSC Advances, vol. 7, no. 25, pp. 15382-15389, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA01267E
V. R. Jeedi, E. L. Narsaiah, M. Yalla, R. Swarnalatha, S. N. Reddy, and A. S. Chary, “Structural and electrical studies of PMMA and PVDF based blend polymer electrolyte,” SN Applied Sciences, vol. 2, no. 12, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03868-8
N. K. Nath, R. R. Mohanta, R. K. Parida, B. N. Parida, and N. C. Nayak, “Structural, morphological, and dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/(Bi0.5Ba0.25Sr0.25)(La0.5Ti0.5)O3 composites,” Journal of Applied Polymer Science, vol. 141, no. 31, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.55729
M. Samet, V. Levchenko, G. Boiteux, G. Seytre, A. Kallel, and A. Serghei, “Electrode polarization vs. Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars interfacial polarization in dielectric spectra of materials: Characteristic frequencies and scaling laws,” The Journal of Chemical Physics, vol. 142, no. 19, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4919877
B. M. Greenhoe, M. K. Hassan, J. S. Wiggins, and K. A. Mauritz, “Universal power law behavior of the AC conductivity versus frequency of agglomerate morphologies in conductive carbon nanotube‐reinforced epoxy networks,” Journal of Polymer Science Part B Polymer Physics, vol. 54, no. 19, pp. 1918-1923, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.24121
S. Tu, Q. Jiang, X. Zhang, and H. N. Alshareef, “Large dielectric constant enhancement in MXene percolative polymer composites,” ACS Nano, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 3369-3377, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b08895
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












