Degradation of wastewater by Advanced Oxidation Processes using green synthesised CuO nanoparticles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v36i1.2467Keywords:
Nanoparticles, Response surface methodology, Brown G, PhotocatalystAbstract
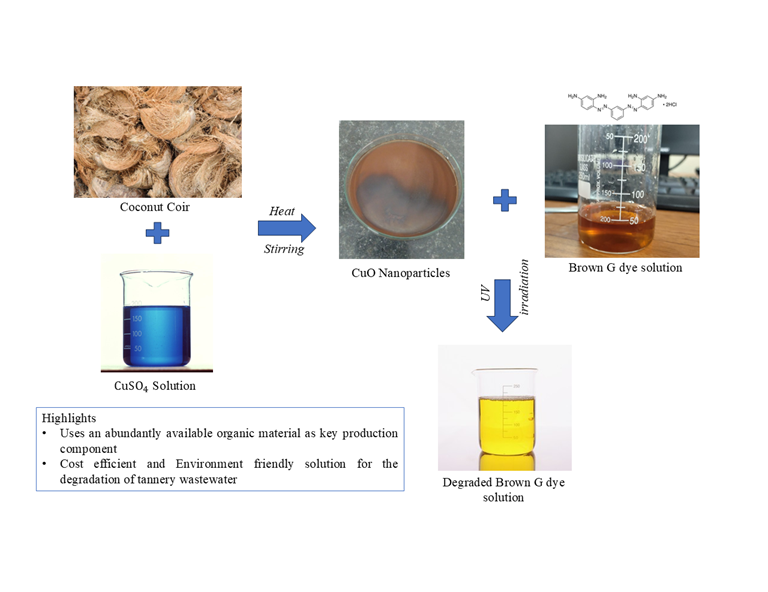
This study highlights the green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using coconut coir extract and evaluates their photocatalytic performance in the degradation of the Brown G dye. The CuO nano-particles were synthesised through sol-gel method, and the biomolecules like polyphenols, tannins and flavonoids acted as reducing agents to stabilise the nanoparticles. The characterisation of these nanoparticles was carried out through XRD, FTIR and FESEM methods. The nanoparticles were used to degrade the dye Brown G under UV irradiation. Response surface methodology was used to optimise the operating parameter with Box-Behnken design, which is the most suitable for varying 3 or more parameters. The parameters varied in this experiment were temperature, catalyst loading and pH. The maximum dye degradation of 80.01% was achieved under the optimised conditions of pH 7, temperature 33.5℃ and at 17.5 mg of CuO catalyst. The kinetic studies of experimental data indicate that the degradation follows a first-order reaction. The results show that the green-synthesised CuO nanoparticles are an effective photocatalyst for treating dye wastewater.
Downloads
References
M. P. Niharika, R. Garlapallya, K. Ruthvik, M. Velaga, and B. Manmadha Rao, “Hydrogen production on g-C3N4 nanoflakes via photoelectrochemical water splitting,” Materials Today: Proceedings, 2023 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.06.188
M. Mathanmohun, S. Sagadevan, Md Z. Rahman, J. A. Lett, I. Fatimah, S. Moharana, S. Garg, and M. A. Al-Anber, “Unveiling sustainable, greener synthesis strategies and multifaceted applications of copper oxide nanoparticles,” Journal of Molecular Structure, vol. 1305, p. 137788, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.137788
K. R. Kaja, S. A. Behera, B. Das, S. Hajra, S. Panda, M. A. Belal, N. Vittayakorn, B. Nanda, P. G. R. Achary, and H. J. Kim, “Calcium copper titanate particles based energy harvesting and removal of pharmaceutical pollutants,” ACS Applied Electronic Materials, vol. 7, no. 9, pp. 4327–4338, 2025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.5c00478
A. Panda, K. K. Das, K. R. Kaja, V. Gandi, S. G. Mohanty, and B. K. Panigrahi, “Low-cost high performance sustainable triboelectric nanogenerator based on laboratory waste,” Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, vol. 35, no. 1, p. e2226, 2025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v35i1.2226
C. Madhusha, T. Jauasundara, I. Munaweera, C. Perera, G. Wijesinghe, M. Weerasekera, C. Sandaruwan, A. Meiyazhagan, F. C. R. Hernandez, P. M. Ajayan, and N. Kottegoda, “Synthesis and structural characterization of copper nanoparticles doped activated carbon derived from coconut coir for drinking water purification,” Materials Today Chemistry, vol. 27, p. 101312, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.101312
A. Panda, K. K. Das, K. R. Kaja, M. Belal, and B. K. Panigrahi, “Single electrode mode triboelectric nanogenerator for recognition of animal sounds,” Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, vol. 34, no. 4, p. 2170, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v34i4.2170
M. D. Moroda, T. Leta Deressa, A. H. Tiwikrama, and T. F. Chala, “Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Rosmarinus officinalis leaf extract and evaluation of its anti-microbial activity,” Next Materials, vol. 7, p. 100337, 2025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nxmate.2024.100337
N. Chakraborty, J. Banerjee, P. Chakraborty, A. Banerjee, S. Chanda, K. Ray, K. Acharya, and J. Sarkar, “Green synthesis of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles and their applications: A review,” Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 187–215, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2022.2025916
H. N. Jayasimha, K. G. Chandrappa, P. F. Sanaulla, and V. G. Dileepkumar, “Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles: A promising material for photocatalysis and electrochemical sensor,” Sensors International, vol. 5, p. 100254, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2023.100254
H. Ahsan, M. Shahid, M. Imran, F. Mahmood, M. H. Siddique, H. M. Ali, M. B. K. Niazi, S. Hussain, M. Shahbaz, M. Ayyub, and T. Shahzad, “Photocatalysis and adsorption kinetics of azo dyes by nanoparticles of nickel oxide and copper oxide and their nanocomposite in an aqueous medium,” Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology, vol. 10, e14358, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.14358
N. M. Mahmoodi, M. Arami, N. Y. Limaee, and N. S. Tabrizi, “Kinetics of heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of reactive dyes in an immobilized TiO2 photocatalytic reactor,” Journal of colloid and interface Science, vol. 295, no. 1, pp. 159-164, 2006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.08.007
A. Fujishima and K. Honda, “Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode,” Nature, vol. 238, no. 5358, pp. 37–38, 1972. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0
M. A. Rauf, and S. S. Ashraf, “Fundamental principles and application of heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of dyes in solution,” Chemical engineering journal, vol. 151, no. 1-3, pp. 10-18, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.02.026
J. Komara, J. P. Karumuri, and B. S. S. Naik, “Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using solanum melongena seeds extract and its applications in degradation of Rose Bengal dye, antibacterial, catalytic reduction and antioxidant activity,” Hybrid Advances, vol. 7, p. 100304, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hybadv.2024.100304
T. Gayathri, S. L. Kumar, S. Sangavi, M. Yudhika, &and M. Swathy, “Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Carica papaya and their antimicrobial activity,” Materials Today: Proceedings, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.11.136
F. H. Hussein, A. F. Halbus, H. A. K. Hassan, and W. A. K. Hussein, “Photocatalytic degradation of bismarck Brown G using irradiated ZnO in aqueous solutions,” Journal of Chemistry, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 540–544, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/719674
A. I. Khuri, and S. Mukhopadhyay, “Response surface methodology, Wiley interdisciplinary reviews,” Computational statistics, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 128-149, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/wics.73
R. H. Myers, “Response surface methodology—current status and future directions,” Journal of quality technology, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 30-44, 1999. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00224065.1999.11979891
J. P. Kleijnen, “Response surface methodology for constrained simulation optimization” An overview,” Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 50-64, 2008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2007.10.001
A. Houas, H. Lachheb, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, C. Guillard, and J-M. Herrmann, “Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water,” Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 145-157, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00276-9
M. Jeevarathinam, and I. V. Asharani, “Synthesis of CuO, ZnO nanoparticles, and CuO-ZnO nanocomposite for enhanced photo-catalytic degradation of Rhodamine B: A comparative study,” Scientific Reports, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 9718, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60008-7
K. Dulta, G. K. Agceli, P. Chauhan, R. Jasrotia, P. K. Chauhan, and J. O. Ighalo, “Multifunctional CuO nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic dye degradation and antibacterial activity,” Sustainable Environment Research, vol. 32, pp. 1-15, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42834-021-00111-w
S. Korpe, B. Bethi, S. H. Sonawane, and K. V. Jayakumar, “Tannery wastewater treatment by cavitation combined with advanced oxidation process (AOP),” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 59, p. 104723, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104723
S. Jiménez, M. Andreozzi, M. M. Micó, M. G. Álvarez, and S. Contreras, “Produced water treatment by advanced oxidation processes,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 666, pp. 12–21, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.128
I. M. F. Cardoso, R. M. F. Cardoso, and J. C. G. E. da Silva, “Advanced oxidation processes coupled with nanomaterials for water treatment,” Nanomaterials, vol. 11, no. 8, p. 2045, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082045
A. T. Nair, A. Makwana, and M. M. Ahammed, “The use of response surface methodology for modelling and analysis of water and wastewater treatment processes: A review,” Water science and technology, vol. 69, no. 3, pp. 464-478, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.733
S. J. M. Breig, and K. J. K. Luti, “Response surface methodology: A review on its applications and challenges in microbial cultures,” Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 42, pp. 2277-2284, 2021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.316
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












