Surface properties and in-vitro bioactivity studies of TiO2 nanowire doped transition metal (M=Fe, Co, and Mn)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v36i1.2527Keywords:
TiO2 nanowire, Fe, Co, Mn, In-vitroAbstract
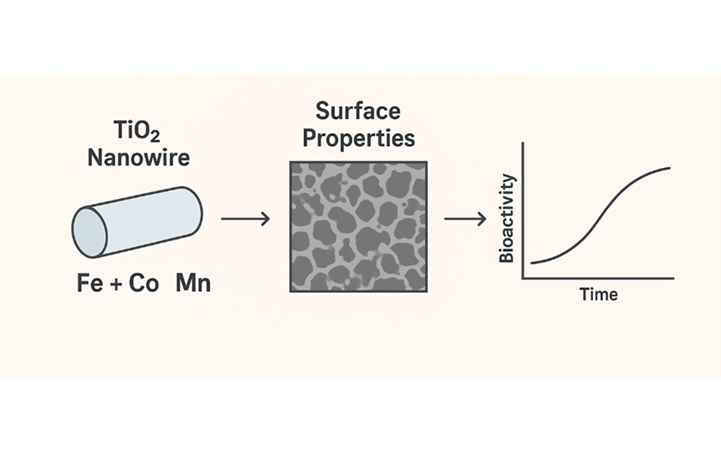
This study investigates the influence of transition metal (Fe, Co, Mn) doping on the surface properties and in-vitro bioactivity of TiO2 nanowires. It aims to elucidate how transition-metal doping alters the surface behavior and biological response of TiO2 nanowires, enabling their potential use in biocompatible and magnetically responsive materials. Magnetic TiO2 nanowires doped with transition metals (Mx+/TiO2) were successfully prepared by a hydrothermal method using titanium dioxide in alkaline solution. Cations were added with Ti/Mx+ molar ratios of 5 to produce Fe/TNW, Co/TNW, and Mn/TNW. Characterization using SEM and XRD determine their surface properties. In-vitro bioactivity tests were conducted by observing the response of C2C12 cells. A cytotoxicity assay determined the effect of TiO2 Nanowires (5 mg∙mL‒1) on C2C12 cell viability at 48 h and 72 h. The results showed that metal-doped TiO2 nanowires did not significantly affect cell activity, and C2C12 cell differentiation remained. In conclusion, transition metal-doped TiO2 nanowires do not affect C2C12 cell activity at certain doses. The magnetic properties of doped TiO2 nanowires open new opportunities for controlled drug delivery using external magnets.
Downloads
References
Z. Wei, M. Endo-Kimura, K. Wang, C. Colbeau-Justin, and E. Kowalska, “Influence of semiconductor morphology on photocatalytic activity of plasmonic photocatalysts: Titanate nanowires and octahedral anatase nanoparticles,” Nanomaterials, vol. 9, no. 10, p. 1447, 2019.
X. Kang, S. Liu, Z. Dai, Y. He, X. Song, and Z. Tan, “Titanium dioxide: From engineering to applications,” Catalysts, vol. 9, no. 2, Art. no. 2, 2019.
M. Rodríguez-Reyes, and H. Dorantes-Rosales, “A simple route to obtain TiO2 nanowires by the sol–gel method,” Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, vol. 59, pp. 658–661, 2011.
H. Shang, and G. Cao, “Template-based synthesis of nanorod or nanowire arrays,” in Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology, B. Bhushan, Ed., Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2007, pp. 161–178.
S. Sabbagh, and M. Behnajady, “Synthesis of TiO2 (B) and high‐temperature stable anatase TiO2 nanowires by hydrothermal method and investigation of photocatalytic activity,” Photo-chemistry and Photobiology, vol. 95, no. 3, pp. 733–739, 2018.
D. Zhang, J. Chen, Q. Xiang, Y.-X. Li, M. Liu, and Y. Liao, “Transition-metal-ion (Fe, Co, Cr, Mn, Etc.) doping of TiO2 nanotubes: A general approach,” Inorganic Chemistry, vol. 58, no. 19, pp. 12511–12515, 2019.
R. Tietze, J. Zaloga, H. Unterweger, S. Lyer, R. P. Friedrich, C. Janko, M. Pöttler, S. Dürr, C. Alexiou, “Magnetic nano-particle-based drug delivery for cancer therapy,” Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, vol. 468, no. 3, pp. 463–470, 2015.
D. Alromi, S. Madani, and A. Seifalian, “Emerging application of magnetic nanoparticles for diagnosis and treatment of cancer,” Polymers, vol. 13, no. 23, p. 4146, 2021.
H. Hu, B. Zhang, L. Li, Q. Guo, D. Yang, X. Wei, X. Fan, J. Liu, Q. Wu, Y. Oh, Y. Feng, K. Chen, C. Wang, L. Hou, and N. Gu, “The toxic effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on plasma glucose metabolism are more severe in developing mice than in adult mice,” Environmental Toxicology, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 443-456, 2019
Z. Chen, S. Han, P. Zheng, 周迪 Zhou Di, S. Zhou, and G. Jia, “Effect of oral exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles on lipid metabolism in Sprague-Dawley rats,” Nanoscale, vol. 12, no. 10, pp. 5973-5986, 2020.
C. Rauch, B. Anne-Christine, J. Deleule, and E. Farge, “C2C12 myoblast/osteoblast transdifferentiation steps enhanced by epigenetic inhibition of BMP2 endocytosis,” American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, vol. 283, pp. C235-43, 2002,
M. Dhupal, J.-M. Oh, D. R. Tripathy, S.-K. Kim, S. B. Koh, and K.-S. Park, “Immunotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles via simultaneous induction of apoptosis and multiple toll-like receptors signaling through ROS-dependent SAPK/JNK and p38 MAPK activation,” International Journal of Nanomedicine, vol. 13, pp. 6735–6750, 2018.
R. Hidayat, G. Fadillah, and S. Wahyuningsih, “A control of TiO2 nanostructures by hydrothermal condition and their application: A short review,” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 578, p. 012031, 2019.
T. Gupta, Samriti, J. Cho, and J. Prakash, “Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2 nanorods: formation chemistry, growth mechanism, and tailoring of surface properties for photocatalytic activities,” Materials Today Chemistry, vol. 20, p. 100428, 2021.
A. Mohd Nor, M. Achoi, M. Mamat, M. Zabidi, S. Abdullah, and M. Rusop, “Synthesis of TiO2 nanowires via hydrothermal method,” Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 51, 2012.
F. Huang, A. Yan, and H. Zhao, “Influences of doping on photocatalytic properties of TiO2 Photocatalyst,” Materials Science, Chemistry, 2016.
B. Barrocas, L. D. Chiavassa, M. Conceição Oliveira, and O. C. Monteiro, “Impact of Fe, Mn co-doping in titanate nanowires photocatalytic performance for emergent organic pollutants removal,” Chemosphere, vol. 250, p. 126240, 2020.
M. Gartner, A. Szekeres, H. Stroescu, D. Mitrea, and M. Covei, “Advanced nanostructured coatings based on doped TiO2 for various applications,” Molecules, vol. 28, no. 23, p. 7828, 2023.
M. Misriyani, E. S. Kunarti, and M. Yasuda, “Synthesis of Mn(II)-Loaded TixSi1-xO4 composite acting as a visible-light driven photocatalyst,” Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, vol. 15, no. 1, Art. no. 1, 2015.
D. Yang, "Titanium dioxide: Material for a sustainable environment," IntechOpen, 2018, 518 page.
Q. Deng, X. Xia, M. Guo, and Y. Gao, “Mn-doped TiO2 nano-powders with remarkable visible light photocatalytic activity,” Materials Letters, vol. 65, pp. 2051–2054, 2011.
F. Wang, Y. Zheng, Q. Chen, Z. Yan, D. Lan, E. Lester, and T. Wu, “A critical review of facets and defects in different MnO2 crystalline phases and controlled synthesis – Its properties and applications in the energy field,” Coordination Chemistry Reviews, vol. 500, p. 215537, 2024.
J. J. Mim, M. Hasan, Md. S. Chowdhury, J. Ghosh, Md. H. Mobarak, F. Khanom, and N. Hossain, “A comprehensive review on the biomedical frontiers of nanowire applications,” Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 8, p. e29244, 2024.
P. Bajaj, J. Rivera, D. Marchwiany, and V. Solovyeva, “Graphene-based patterning and differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts,” Advanced Healthcare Materials, vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 995-1000, 2014.
K. Ishizaki, Y. Sugita, F. Iwasa, H. Minamikawa, T. Ueno, M. Yamada, T. Suzuki, and T. Ogawa, “Nanometer-thin TiO2 enhances skeletal muscle cell phenotype and behavior,” International Journal of Nanomedicine, vol. 6, pp. 2191–2203, 2011.
M. Ferrante, A. Grasso, R. Salemi, M. Libra, B. Tomasello, M. Fiore, and C. Copat, “DNA damage and apoptosis as in-vitro effect biomarkers of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2-NPs) and the food additive E171 toxicity in colon cancer cells: HCT-116 and Caco-2,” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 20, no. 3, p. 2002, 2023.
R. Kandikonda, G. Murugadoss, N. Venkatesh, S. S. V. Subbaraj, D. Palani, S. Thota, R. K. Rajaboina, H. Divi, M. Dhayalan, A. Phanumartwiwath, C. R. Mallu, and U. K. Khanapuram, “Redox-driven synthesis of stable copper nanoparticles via metal displacement and their application in organic dye degradation,” Advanced Materials, vol. 6, pp. 9575‒9589, 2025,
X. Chen, W.Liu, and T. Zhang, "Magnetic TiO2 nanowires doped with transition metals for biocompatible applications in muscle tissue engineering," Nanomaterials, vol. 13, no. 3, p. 514, 2023.
H. Wang, Z. Luo, and F. Yang, "Effect of Fe and Co doping on the surface properties and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanostructures," Applied Surface Science, vol. 558, p. 149827, 2021.
Y. Li, C. Zhao, and Q. Liu, "Metal-doped TiO2 nanostructures modulate myoblast adhesion and differentiation via MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways," ACS Applied Bio Materials, vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 4284–4295, 2020.
Y. Zhang, J. Lin, and C. Wu, "Surface-engineered nanostructures for skeletal muscle regeneration: Mechanisms of adhesion and differentiation control," Advanced Healthcare Materials, vol. 11, no. 15, p. 2200249, 2022.
M. Jang, J. Scheffold, L. M. Røst, H. Cheon, and P. Bruheim, “Serum-free cultures of C2C12 cells show different muscle phenotypes which can be estimated by metabolic profiling,” Scientific Reports, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 827, 2022.
B. Geiger, R. Boujemaa-Paterski, S. E. Winograd-Katz, J. B. Venghateri, W.-L. Chung, and O. Medalia, “The Actin network interfacing diverse integrin-mediated adhesions,” Biomolecules, vol. 13, no. 2, Art. no. 2, 2023.
A. V. Vakhrusheva, A. V. Murashko, E. S. Trifonova, Yu. M. Efremov, P. S. Timashev, and O. S. Sokolova, “Role of actin-binding proteins in the regulation of cellular mechanics,” European Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 101, no. 3, p. 151241, 2022.
S. H. Lee, J. H. Kim, and Y. K. Kim, “Role of the fusion index in evaluating myoblast differentiation and myotube formation,” Applied Sciences, vol. 10, no. 14, p. 4864, 2020.
B. Huang, Y. Jiao, Y. Zhu, Z. Ning, Z. Ye, Q. X. Li, C. Hu, and C. Wang, “Mdfi promotes C2C12 cell differentiation and positively modulates fast-to-slow-twitch muscle fiber trans-formation,” Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, vol. 9, p. 605875, 2021.
Y. Wang, Z. Wu, H. Li, and Z. Sun, Quantitative real-time PCR normalization and efficiency analysis in C2C12 myogenic differentiation, Genes & Genomics, vol. 44, no. 9, pp. 1053–1062, 2022.
S. Y. Park, E. Choi, and Y. J. Kim, “Evaluation of nanomaterial cytotoxicity in C2C12 cells using MTT and live/dead assays under magnetic stimulation,” Toxicology Reports, vol. 10, pp. 320–331, 2023.
M. A. Rahman, R. Li, and H. R. Kim, “Assessing cell viability and oxidative stress in nanomaterial-treated myoblasts,” Bio-materials Advances, vol. 136, p. 212780, 2022.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












