Designing biphasic nanocellulose hydrogels to mimic the complex cartilage-bone interface
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v34i4.2066คำสำคัญ:
Bacterial cellulose, Hydroxyapatite, Biomineralization, Hydrogel, osteochondroบทคัดย่อ
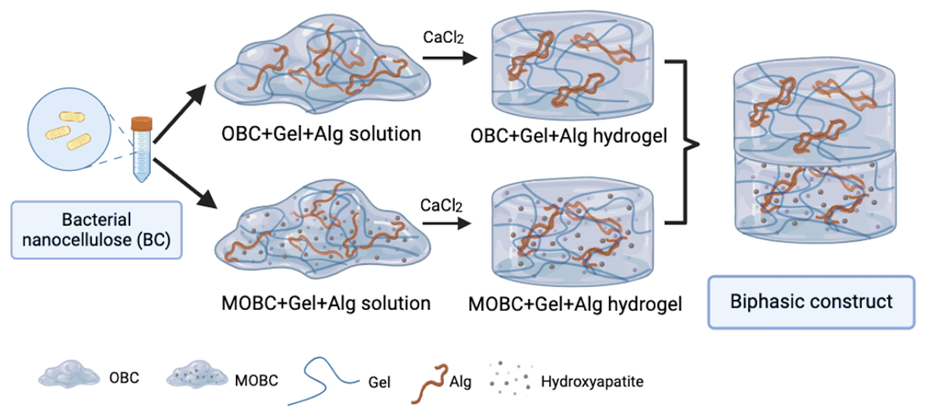
Osteochondral lesions, which affect both the cartilage and the bone, present significant challenges in treatment due to the complex mechanical and biochemical properties of these tissues. A crucial consideration in developing tissue replacements for these lesions is the simultaneous regeneration of cartilage and calcified cartilage, which forms the transition zone to bone. Our current study aims to fabricate a bilayer polymeric hydrogel designed not only to support cartilage regeneration but also to serve as an interface between cartilage and bone. The bilayer hydrogel was created by combining oxidized bacterial nanocellulose, gelatin, and alginate in one layer, while the other layer consisted of the same three biopolymers and hydroxyapatite. The bacterial nanocellulose was effectively oxidized (20%) with sodium periodate and then mineralized with calcium and phosphorus (Ca/P ratio = 0.97), as confirmed by EDX analysis. Remarkably, both layers of the biphasic hydrogel demonstrated cytocompatibility with chondrocytes. Moreover, the addition of hydroxyapatite significantly improved the mechanical strength from 72 kPa (OBC/Gel/Alg) to 90 kPa (MOBC/Gel/Alg). This bilayer hydrogel holds promise for promoting bone-cartilage integration and has the potential to contribute to the healing of osteochondral defects, offering new possibilities in the field of orthopedic tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
J. F. Mano, and R. L. Reis, “Osteochondral defects: present situation and tissue engineering approaches,” Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 261-273, 2007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/term.37
N. Maffulli, U. G. Longo, N. Gougoulias, D. Caine, and V. Denaro, “Sport injuries: A review of outcomes,” British Medical Bulletin, vol. 97, no. 1, pp. 47-80, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldq026
A. H. Gomoll, H. Madry, G. Knutsen, N. van Dijk, R. Seil, M. Brittberg, and E. Kon, "The subchondral bone in articular cartilage repair: current problems in the surgical management,” Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 434-447, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1072-x
B. Zhang, J. Huang, and R. J. Narayan, “Gradient scaffolds for osteochondral tissue engineering and regeneration,” Journal of Materials Chemistry B, vol. 8, no. 36, pp. 8149-8170, 2020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TB00688B
B. Ye, B. Wu, Y. Su, T. Sun, and X. Guo, “Recent advances in the application of natural and synthetic polymer-based scaffolds in musculoskeletal regeneration,” Polymers, vol. 14, no. 21, p. 4566, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214566
G. Satchanska, S. Davidova, and P. D. Petrov, "Natural and synthetic polymers for biomedical and environmental applications," Polymers, vol. 16, no. 8, p. 1159, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081159
I. Gorroñogoitia, U. Urtaza, A. Zubiarrain-Laserna, A. Alonso-Varona, and A. M. Zaldua, "A study of the printability of alginate-based bioinks by 3D bioprinting for articular cartilage tissue engineering," Polymers, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 354, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020354
C. E. G. Garcia, B. Lardy, F. Bossard, F. A. S. Martínez, and M. Rinaudo, "Chitosan based biomaterials for cartilage tissue engineering: Chondrocyte adhesion and proliferation," Food Hydrocolloids for Health, vol. 1, p. 100018, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fhfh.2021.100018
Z. Montaseri, S. S. Abolmaali, A. M. Tamaddon, and F. Farvadi, "Composite silk fibroin hydrogel scaffolds for cartilage tissue regeneration," Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, vol. 79, p. 104018, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.104018
M. A. Salati, J. Khazai, A. M. Tahmuri, A. Samadi, A. Taghizadeh, M. Taghizadeh, P. Zarrintaj, J. D. Ramsey, S. Habibzadeh, F. Seidi, M. R. Saeb, and M. Mozafari, "Agarose- based biomaterials: opportunities and challenges in cartilage tissue engineering," Polymers (Basel), vol. 12, no. 5, p. 1150, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051150
S. Barbon, M. Contran, E. Stocco, S. Todros, V. Macchi, R. De Caro, and A. Porzionato, "Enhanced biomechanical properties of polyvinyl alcohol-based hybrid scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering," Processes, vol. 9, no. 5, p. 9050730, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050730
A. M. Arnold, B. D. Holt, L. Daneshmandi, C. T. Laurencin, and S. A. Sydlik, "Phosphate graphene as an intrinsically osteoinductive scaffold for stem cell-driven bone regeneration," Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, vol. 116, no. 11, pp. 4855-4860, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1815434116
M.-X. Yao, Y.-F. Zhang, W. Liu, H.-C. Wang, C. Ren, Y.-Q. Zhang, T.-L. Shi, and W. Chen, "Cartilage tissue healing and regeneration based on biocompatible materials: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis from 1993 to 2022," Front Pharmacol, vol. 14, pp. 1276849, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1276849
D. Khayatan, A. B. Oskouei, M. Alam, M. Mohammadikhah, A. Badkoobeh, M. Golkar, K. Abbasi, S. Karami, R. S. Soufdoost, and L. K. Hakim, A. Hussain, H. Tebyaniyan, and A. Heboyan, "Cross talk between cells and the current bioceramics in bone regeneration: A comprehensive review," Cell Transplant, vol. 33, p. 09636897241236030, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/09636897241236030
W. Wei, and H. Dai, "Articular cartilage and osteochondral tissue engineering techniques: Recent advances and challenges," Bioactive Materials" vol. 6, no. 12, pp. 4830-4855, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.05.011
P. P. Phatchayawat, A. Khamkeaw, S. Yodmuang, and M. Phisalaphong, "3D bacterial cellulose-chitosan-alginate-gelatin hydrogel scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering," Biochemical Engineering Journal, vol. 184, p. 108476, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2022.108476
N. F. Vasconcelos, F. K. Andrade, L. d. A. P. Vieira, R. S. Vieira, J. M. Vaz, P. Chevallier, D. Mantovani, M. d. F. Borges, and M.F. Rosa, "Oxidized bacterial cellulose membrane as support for enzyme immobilization: properties and morphological features," Cellulose, vol. 27, no. 6, pp. 3055-3083, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-02966-5
E. Tsanaktsidou, O. Kammona, and C. N. Kiparissides, "Recent developments in hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering applications," Polymers, vol. 14, no. 4, p. 839, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040839
Y. Wan, L. Hong, S. Jia, Y. Huang, Y. Zhu, Y. Wang, H. J. Jiang, “Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite–bacterial cellulose nanocomposites,” Composites Sciencd and Technology, vol. 66, no. 11-12, pp. 1825-1832, 2006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.11.027
P. M. Favi, S. P. Ospina, M. Kachole, M. Gao, L. Atehortua, and T. J. Webster, "Preparation and characterization of bio-degradable nano hydroxyapatite–bacterial cellulose composites with well-defined honeycomb pore arrays for bone tissue engineering applications," Cellulose, vol. 23, pp. 1263-1282, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0867-4
K. Pommerening, H. Rein, D. Bertram, and R. Müller, "Estimation of dialdehyde groups in 2, 3-dialdehyde bead-cellulose," Carbohydrate Research, vol. 233, pp. 219-223, 1992. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6215(00)90933-9
P. Roychowdhury, and V.Kumar, "Fabrication and evaluation of porous 2,3‐dialdehydecellulose membrane as a potential biodegradable tissue‐engineering scaffold," Journal of biomedical Material Research: Part A, vol. 76, no. 2, pp. 300-309, 2006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.30503
Z. Li, X. Chen, C. Bao, C. Liu, C. Liu, D. Li, H. Yan, and Q. Lin, "Fabrication and evaluation of alginate/bacterial cellulose nanocrystals–chitosan–gelatin composite scaffolds," Molecules, vol. 26, no. 16, p. 5003, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165003
M. N. Egorikhina, I. I. Bronnikova, Y. P. Rubtsova, I. N. Charykova, M. L. Bugrova, D. D. Linkova, and D. Y. Aleynik, "Aspects of in vitro biodegradation of hybrid fibrin–collagen scaffolds," Polymers, vol. 13, no. 20, p. 13203470, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203470
H. Yan, D. Huang, X. Chen, H. Liu, Y. Feng, Z. Zhao, Z. Dai, X. Zhang, and Q. Lin, "A novel and homogeneous scaffold material: Preparation and evaluation of alginate/bacterial cellulose nanocrystals/collagen composite hydrogel for tissue engineering," Polymer Bulletin, vol. 75, no. 7, pp. 1-16, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2077-0
Y. Yu, W. Guo, J. Qu, S. Wang, X. Wang, Y. He, Y. Yang, Q. He, X. Liu, "Preparation and characterization of dialdehyde cellulose nanocrystals from the waste nutshell," Environment, Development and Sustainability, vol. 1, pp. 1-17, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04332-4
J. Sugiyama, J. Persson, and H. Chanzy, "Combined infrared and electron diffraction study of the polymorphism of native celluloses," Macromolecules, vol. 24, no. 9, pp. 2461-2466, 1991. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00009a050
J. Wu, Y. Zheng, Z. Yang, Q. Lin, K. Qiao, X. Chen, and Y. Peng, "Influence of dialdehyde bacterial cellulose with the nonlinear elasticity and topology structure of ECM on cell adhesion and proliferation," RSC Advances, vol. 4, no. 8, pp. 3998-4009, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA45407J
U. J. Kim, S. Kuga, M. Wada, T. Okano, and T. Kondo, "Periodate oxidation of crystalline cellulose," Biomacromolecules, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 488-492, 2000. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bm0000337
Q. Fan, D. Lewis, and K. N. Tapley, "Characterization of cellulose aldehyde using Fourier transform infrared spectro-scopy," Journal of Applied Polymer Science, vol. 82, no. 5, pp. 1195-1202, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1953
L. M. de Vasconcelos, N. Vasconcelos, D. Lomonaco, M. de Freitas Rosa, E. Rodriguez-castellon, F. K. Andrade, and R. S. Vieira, "Microwave-assisted periodate oxidation as a rapid and efficient alternative to oxidize bacterial cellulose wet membrane," Polymer Bulletin, vol. 80, pp. 11861-11881, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04617-0
E. Höglund, "Production of dialdehyde cellulose and periodate regeneration: Towards feasible oxidation processes," Chemical Sciences, p. 36, 2015
J. Li, Y. Wan, L. Li, H. Liang, and J. Wang, "Preparation and characterization of 2,3-dialdehyde bacterial cellulose for potential biodegradable tissue engineering scaffolds," Materials Science and Engineering: C, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 1635-1642, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2009.01.006
Y. Wan, Y. Huang, C. D. Yuan, S. Raman, Y. Zhu, H. J. Jiang, F. He, and C. Gao, "Biomimetic synthesis of hydroxyapatite/ bacterial cellulose nanocomposites for biomedical applications," Materials Science and Engineering: C, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 855-864, 2007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2006.10.002
F. Nurlidar, E. Budianto, D. Darwis, and Sugiarto, "Hydroxy-apatite deposition on modified bacterial cellulose matrix," Macromolecular Symposia"vol. 353, no. 1, pp. 128-132, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201550317
A. Cañas-Gutiérrez, L. Toro, C. Fornaguera, S. Borrós, M. Osorio, C. Castro-Herazo, and D. Arboleda-Toro, "Biomineralization in three-dimensional scaffolds based on bacterial nanocellulose for bone tissue engineering: Feature characterization and stem cell differentiation," Polymers, vol. 15, no. 9, p. 15092012, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092012
X. Song, C. Zhu, D. Fan, Y. Mi, X. Li, R. Z. Fu, Z. Duan, Y. Wang, and R. R. Feng, "A novel human-like collagen hydrogel scaffold with porous structure and sponge-like properties," Polymer (Basel), vol. 9, no. 12, p. 638, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120638
Z. Li, H. Liu, Y. Liao, H. Wang, X. Sun, X. Chen, H. Yan, and Q. Lin, "Design and properties of alginate/gelatin/ cellulose nano-crystals interpenetrating polymer network composite hydrogels based on in situ cross-linking," European Polymer Journal, vol. 201, pp. 112556, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2023.112556
F. Farshi Azhar, A. Olad, and R. Salehi, "Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-gelatin/nanohydroxyapatite-polyaniline composite with potential application in tissue engineering scaffolds," Designed Monomers and Polymers, vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 654-667, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15685551.2014.907621
E. P. C. G. Luz, P. H. S. Chaves, L. d. A. P. Vieira, S. F. Ribeiro, M. de Fátima Borges, F. K. Andrade, C. R. Muniz, A. Infantes-Molina, E. Rodríguez-Castellón, M. de Freitas Rosa, and R. S. Vieira, "In vitro degradability and bioactivity of oxidized bacterial cellulose-hydroxyapatite composites," Carbohydrate Polymers, vol. 237, p. 116174, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116174
W. Habraken, P. Habibovic, M. Epple, and M. Bohner, "Calcium phosphates in biomedical applications: materials for the future?," Materials Todey, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 69-87, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.10.008
H. Wang, B. Hu, H. Li, G. Feng, S. Pan, Z. Chen, B. Li, and J. Song, "Biomimetic mineralized hydroxyapatite nanofiber-incorporated methacrylated gelatin hydrogel with improved mechanical and osteoinductive performances for bone regeneration," International Journal of Nanomedicine, vol. 17, pp. 1511-1529, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S354127
W. Treesuppharat, P. Rojanapanthu, C. Siangsanoh, H. Manuspiya, and S. Ummartyotin, "Synthesis and characterization of bacterial cellulose and gelatin-based hydrogel composites for drug-delivery systems," Biotechnology Reports, vol. 15, pp. 84-91, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.07.002
C. Kaliampakou, N. Lagopati, E. A. Pavlatou, and C. A. Charitidis, "Alginate–gelatin hydrogel scaffolds; An optimization of post-printing treatment for enhanced degradation and swelling behavior," Gels, vol. 9, no. 11, p. 857, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110857
M. Singh, A. R. Ray, and P. Vasudevan, "Biodegradation studies on periodate oxidized cellulose," Biomaterials, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 16-20, 1982. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(82)90055-2
A. J. Kerin, M. R. Wisnom, and M. A. Adams, "The compressive strength of articular cartilage," Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine, vol. 212, no. 4, pp. 273-280, 1998. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1243/0954411981534051
A. T. Estevez, T. Alberto, and Y. Abdallah, "Biomimetic approach for enhanced mechanical properties and stability of self-mineralized calcium phosphate dibasic–sodium alginate–gelatine hydrogel as bone replacement and structural building material," Processes, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 944, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050944
W. Ma, M. Yang, C. Wu, S. Wang, and M. Du, "Bioinspired self-healing injectable nanocomposite hydrogels based on oxidized dextran and gelatin for growth-factor-free bone regeneration," International Journal of Biological Macro-molecules, vol. 251, pp. 126145, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126145
M. Suhail, J.-Y. Liu, M.-C. Hung, I.-H. Chiu, M. U. Minhas, and P.-C. Wu, "Preparation, in vitro characterization, and cyto-toxicity evaluation of polymeric pH-responsive hydrogels for controlled drug release," Pharmaceutics, vol. 14, no. 9, p. 1864, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091864
Y. Ma, X. Wang, T. Su, F. Lu, Q. Chang, and J. Gao, "Recent advances in macroporous hydrogels for cell behavior and tissue engineering," Gels, vol. 8, no. 10, p. 606, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100606
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
วิธีการอ้างอิง
การอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารโลหะ, วัสดุ และแร่

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












