Enhanced photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) under visible light a magnetically separable TiO\(_{2}\)-Fe/Fe\(_{3}\)O\(_{4}\) photocatalyst prepared from iron rusty waste
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v35i1.2162คำสำคัญ:
Photoreduction, TiO2, doping, Fe3O4, rusty wasteบทคัดย่อ
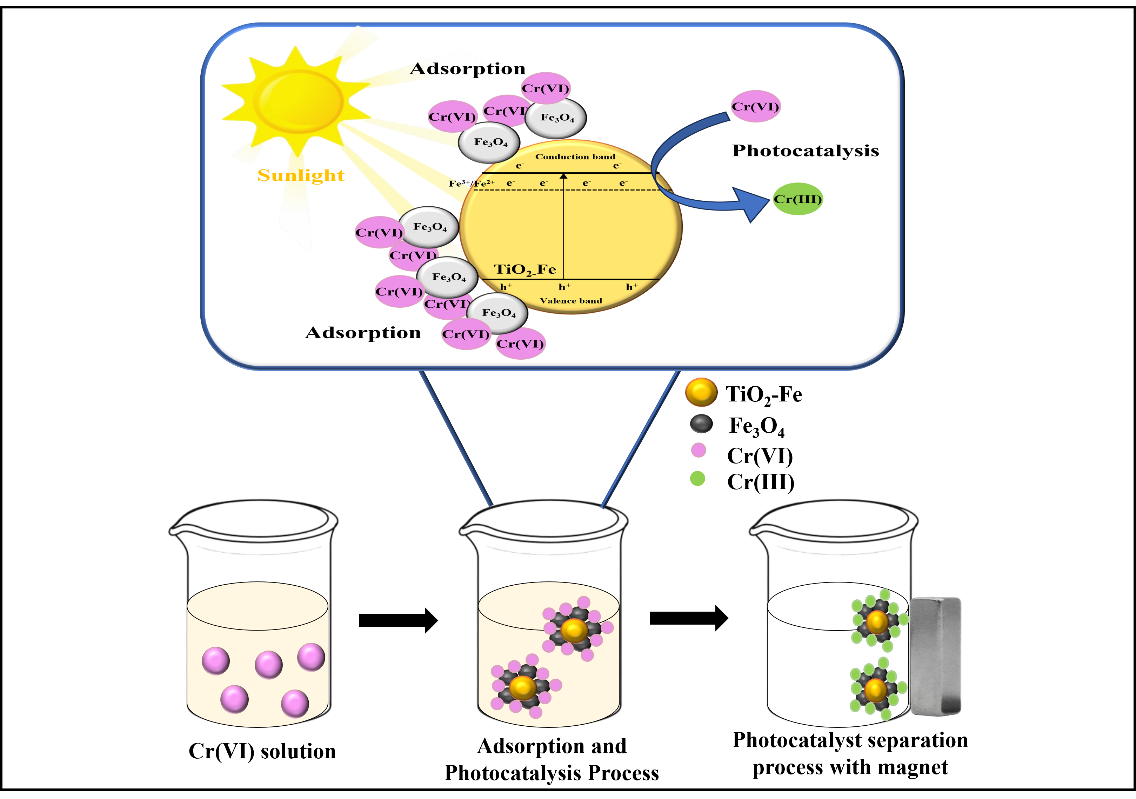
This research deals with enhancing the visible activity and generating the magnetic property of TiO2 by Fe doping and Fe3O4 impregnation respectively, using rusty iron waste as Fe source. The prepared TiO2-Fe/Fe3O4 photocatalysts were characterized by SR-UV/Visible, FTIR, XRD, and SEM-EDX instruments. The resulting photocatalysts are responsive to visible light and can be separated magnetically and used for photoreduction of Cr (VI) ions. In the photoreduction of Cr(VI) over TiO2-Fe/Fe3O4 photo-catalysts with various amounts of Fe dopant and alteration of Fe3O4 fraction, the photocatalyst mass, irradiation time, and solution pH were optimized. The research results assign that doping Fe to TiO2 photo-catalysts can decrease the band gap energy (Eg) consequently improving its activity under visible irradiation. Furthermore, the magnetization of TiO2-Fe allows it to be separated practically and effectively. The best detachable and the most active photocatalyst is shown by TiO2-Fe/Fe3O4 having a Ti/Fe mole ratio of 1:0.05 and Fe3O4 fraction of 50.00%. The highest photo-reduction of Cr(VI) 10 mg∙L‒1 in 100 mL solution, 92.5%, can be achieved by applying 0.2 g of the photocatalyst mass, solution pH 3, in 90 min of reaction time under visible light.
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
J. Zhang, S. Lin, M. Han, Q. Su, L. Xia, and Z. Hui, “Adsorption properties of magnetic magnetite nanoparticle for coexistent Cr(VI) and Cu(II) in mixed solution,” Water (Switzerland), vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1-13, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020446
H. Karimi-Maleh, A. Ayati, S. Ghanbari, Y. Orooji, B. Tanhaei, F. Karimi, M. Alizadeh, J. Rouhi, L. Fu, and M. Sillanpaa, “Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr(VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: A comprehensive review,” Journal of Molecular Liquids, vol. 329, p. 115062, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115062
E. Prabakaran, and K. Pillay, “Self-assembled silver nano-particles decorated on exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride/carbon sphere nanocomposites as a novel catalyst for catalytic reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) from wastewater and reuse for photocatalytic applications,” ACS Omega, vol. 6, no. 51, pp. 35221-35243, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00866
J. Ding, L. Pu, Y. Wang, B. Wu, A. Yu, X. Zhang, C. Pan, Q. Zhang, and G. Gao, “Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) together with Cr(III) sequestration by polyaniline confined in pores of polystyrene beads,” Environmental Science and Technology, vol. 52, no. 21, pp. 12602-12611, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02566
R. Acharya, B. Naik, and K. Parida, “Cr(VI) remediation from aqueous environment through modified-TiO2-mediated photo-catalytic reduction,” Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1448-1470, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.137
R. Djellabi, P. Su, E. A. Elimian, V. Poliukhova, S. Nouacer, I. A. Abdelhafeez, N. Abderrahim, D. Aboagye, V. V. Andhalkar, W. Nabgan, S. Rtimi, and S. Contreras, “Advances in photo-catalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium: From fundamental concepts to materials design and technology challenges,” Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 50, p. 103301, 2022.
E. T. Wahyuni, and N. H. Aprilita, “Photoreduction processes over TiO2 photocatalyst,” Photocatalysts - Applications and Attributes, p. 80914, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.80914
R. Djellabi, F. M. Ghorab, S. Nouacer, A. Smara, and O. Khireddine, “Cr(VI) photocatalytic reduction under sunlight followed by Cr(III) extraction from TiO2 surface,” Materials Letters, vol. 176, pp. 106-109, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.04.090
Z. Wu, X. Liu, C. Yu, F. Li, W. Zhou, and L. Wei, “Construct interesting CuS/TiO2 architectures for effective removal of Cr(VI) in simulated wastewater via the strong synergistic adsorption and photocatalytic process,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 796, p. 148941, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148941
Z. Chen, J. Ma, K. Yang, S. Feng, W. Tan, Y. Tao, H. Mao, and Y. Kong, “Preparation of S-doped TiO2-three dimensional graphene aerogels as a highly efficient photocatalyst,” Synthetic Metals, vol. 231, pp. 51-57, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2017.06.020
M. Hamadanian, A. Reisi-Vanani, P. Razi, S. Hoseinifard, and V. Jabbari, “Photodeposition-assisted synthesis of novel nanoparticulate In, S-codoped TiO2 powders with high visible light-driven photocatalytic activity,” Applied Surface Science, vol. 285, no. Part B, pp. 121-129, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.07.165
Y. Li, P. Zhang, J. Zhang, H. Zhang, T. Ai, Z. Zhao, Y. Liu, Z. Pu, “Photocatalytic performance of Fe doped TiO2 on the surface of carbon fiber,” Optical Materials, vol. 133, no. 13 p. 112970, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.112970
T. Jiang, J. Chai, Y. Wang, Q. Du, J. Shi, and Z. Xu, “Enhanced photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using Fe0/TiO2-based polymeric nanocomposites,” Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 30, no. 51, pp. 110312-110323, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30106-6
I. Mironyuk, N. Danyliuk, T. Tatarchuk, I. Mykytyn, and V. Kotsyubynsky, “Photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye using Fe-doped TiO2 nanocatalysts,” Physics and Chemistry of Solid State, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 697-710, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15330/pcss.22.4.697-710
K. Vijayalakshmi, and S. D. Jereil, “Influence of Fe catalytic doping on the properties of TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by microwave method,” Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, vol. 25, no. 11, pp. 5089-5094, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2276-5
S. C. Xu, S. S. Pan, Y. Xu, Y. Y. Luo, Y. X. Zhang, and G. H. Li, “Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater under sunlight by Fe(II)-doped TiO2 spherical shell,” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 283, pp. 7-13, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.071
J. C. Te Lin, M. D. G. de Luna, M. J. N. Gotostos, and M. C. Lu, “Effects of doping amounts of potassium ferricyanide with titanium dioxide and calcination durations on visible-light degradation of pharmaceuticals,” Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 23, no. 22, pp. 22721-22733, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7470-y
E. T. Wahyuni, N. D. Lestari, I. R. Cinjana, S. Annur, T. A. Natsir, and M. Mudasir, “Doping TiO2 with Fe from iron rusty waste for enhancing its activity under visible light in the Congo red dye photodegradation,” Journal of Engineering and Applied Science, vol. 70, no. 1, pp. 1-14, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s44147-023-00178-9
S. Al-Salihi, M. Bayati, A. M. Jasim, M. M. Fidalgo, and Y. Xing, “Magnetic mesoporous TiO2/Fe3O4 nanocomposite adsorbent for removal of sulfamethazine from water,” Environmental Advances, vol. 9, p. 100283, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2022.100283
M. M. Ba-Abbad, A. Benamour, D. Ewis, A. W. Mohammad, and E. Mahmoudi, “Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different shapes through a co-precipitation method and their application,” Jom, vol. 74, no. 9, pp. 3531-3539, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05380-3
M. H. Lee, J. H. Park, H. S. Han, H. J. Song, I. S. Cho, J. H. Noh, and K. S. Hong, “Nanostructured Ti-doped hematite (α-Fe2O3) photoanodes for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation,” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, vol. 39, no. 30, pp. 17501-17507, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.10.031
J. Xiao, A. M. Oliveira, L. Wang, Y. Zhao, T. Wang, J. Wang, B. P. Setzler, and Y. Yan, “Water-fed hydroxide exchange membrane electrolyzer enabled by a fluoride-incorporated nickel−iron oxyhydroxide oxygen evolution electrode,” ACS Catalysis, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 264-270, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c04200
M. Shaban, M. Binsabt, A. M. Ahmed, and F. Ewis, “Recycling rusty iron with natural zeolite heulandite to create a unique nanocatalyst for green hydrogen production,” Nanomaterials, vol. 11, no. 12, p. 3445, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123445
N. H. Dahon, M. J. Kassim, N. Nu’Aim Razali, E. M. F. M. Yuslee, A. A. Nasrullah, and N. F. Basri,, “FTIR analysis on phase transformation of rust in the presence of gambir,” Journal of Global Scientific Research, vol. 1, pp. 54-62, 2018.
M. Jia, P. Hu, and G. Hu, “Corrosion layers on archaeological cast iron from nanhai I,” Materials, vol. 15, no. 14, p. 4980, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144980
C. Rémazeilles, and P. Refait, “Fe(II) hydroxycarbonate Fe2(OH)2CO3 (chukanovite) as iron corrosion product: Synthesis and study by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy,” Polyhedron,vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 749-756, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2008.12.034
K. Wang, Y. Zhuo, J. Chen, D. Gao, Y. Ren, C. Wang, and Z. Qi, “Crystalline phase regulation of anatase-rutile TiO2 for the enhancement of photocatalytic activity,” RSC Advances, vol. 10, no. 71, pp. 43592-43598, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA09421H
S. Sood, A. Umar, S. K. Mehta, and S. K. Kansal, “Highly effective Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles photocatalysts for visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic compounds,” Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, vol. 450, pp. 2130-223, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.03.018
R. Ebrahimi, A. Maleki, R. Rezaee, H. Daraei, M. Safari, G. Mckay, S-M. Lee, and A. Jafari, “Synthesis and application of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for photodegradation of 2,4-D from aqueous solution,” Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, vol. 46, no. 7, pp. 6409-6422, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05071-8
M. B. Marami, M. Farahmandjou, and B. Khoshnevisan, “Sol–gel synthesis of Fe-doped TiO2 nanocrystals,” Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 3741-3748, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6234-5
A. F. Shojaei, A. Shams-Nateri, and M. Ghomashpasand, “Magnetically recyclable Fe3+/TiO2@Fe3O4 nanocomposites towards degradation of direct blue 71 under visible-light irradiation,” Micro and Nano Letters, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 161-165, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2016.0620
A. Malik, S. Hameed, M. J. Siddiqui, M. M. Haque, and M. Muneer, “Influence of ce doping on the electrical and optical properties of TiO2 and its photocatalytic activity for the degradation of remazol brilliant blue R,” International Journal of Photoenergy, vol. 2013, no. 2, p. 1-9, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/768348
W. H. Saputera, A. F. Amri, R. Daiyan, and D. Sasongko, “Photocatalytic technology for palm oil mill effluent (POME) wastewater treatment: Current progress and future perspective,” Materials, vol. 14, no. 11, p. 2846, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112846
V. A. R. Villegas, J. D. L. Ramírez, E. H. Guevara, S. P. Sicairos, L. A. H. Ayala, and B. L. Sanchez, “Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles for photocatalysis of nitrobenzene,” Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 223-235, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2019.12.004
Q. Zhang, L. Yu, C. Xu, W. Zhang, M. Chem, Q. Xu, and G. Diao, “A novel method for facile preparation of recoverable Fe3O4@TiO2 core-shell nanospheres and their advanced photo-catalytic application,” Chemical Physics Letters, vol. 761, p. 138073, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2020.138073
Y. Feng, V. D. Kreslavski, A. N. Shmarev, A. A. Ivanov, S. K. Zharmukhamedov, A. A. Kosobryukhov, M. Yu, S. I. Allakhverdiev, and S. Shabala, “Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) on growth, photosynthesis, antioxidant activity and distribution of mineral elements in wheat (triticum aestivum) plants,” Plants, vol. 11, no. 14, p. 1894, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11141894
N. Madima, K. K. Kefeni, S. B. Mishra, A. K. Mishra, and A. T. Kuvarega, “Fabrication of magnetic recoverable Fe3O4/ TiO2 heterostructure for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye.,” Inorganic Chemistry Communications. vol. 145, no. 1, p. 109966, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109966
A. C. Chu, R. S. Sahu, T. H. Chou, and Y. H. Shih, “Magnetic Fe3O4@TiO2 nanocomposites to degrade bisphenol A, one emerging contaminant, under visible and long wavelength UV light irradiation,” Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 105539, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105539
N. H. Mthombeni, M. S. Onyango, and O. Aoyi, “Adsorption of hexavalent chromium onto magnetic natural zeolite-polymer composite,” Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, vol. 50, pp. 242-251, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.037
D. Arista, A. Rachmawati, N. Ramadhani, R. E. Saputro, A. Taufiq, and Sunaryono, “Antibacterial performance of Fe3O4/ PEG-4000 prepared by co-precipitation route,” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 515, p. 012085, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/515/1/012085
F. Heidarinejad, H. Kamani, and A. Khtibi, “Magnetic Fe-doped TiO2@Fe3O4 for metronidazole degradation in aqueous solutions: Characteristics and efficacy assessment.,” Heliyon. vol. 9, no. 11, p. e21414, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21414
X. Yuan, X. Wu, Z. Feng, W. Jia, X. Zheng, and C. Li, “Facile synthesis of heterojunctioned ZnO/Bi2S3 nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic reduction of aqueous Cr(Vi) under visible-light irradiation,” Catalysts, vol. 9, no. 7, pp. 1-14, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070624
J. Preethi, M. H. Farzana, and S. Meenakshi, “Photo-reduction of Cr(VI) using chitosan supported zinc oxide materials,”
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 104, no. Part B, pp. 1783-1793, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.082
B. Zhao, H. Xu, K. Zhang, B. Gao, Y. Wang, Q. Wang, K. Zhang, Y. Huang, and J. Ii, “Visible-light-driven CQDs/TiO2 photocatalytic simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and organics: Cooperative reaction, kinetics and mechanism,” Chemosphere, vol. 307, no. Part 2, p. 135897, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135897
A. Prastika, and I. Alamsah, “Kinetika adsorpsi asam tanat pada fotokatalis SiO2/TiO2,” Jurnal teknologi terapan, vol. 06, no. 1, pp. 14-22, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33379/gtech.v6i1.1241
Y. Yuniar, E. T. Wahyuni, and N. H. Aprilita, “Photoreduction of Cr(VI) Catalyzed by TiO2-Lignin.,” Indonesian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Chemistry. vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 22-27, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24845/ijfac.v2.i1.22
R. Djellabi, P. Su, A. Elimian, V. Poliukhova, S. Nouacer, I. A. Abdelhafeez, N. Abderrahim, D. Aboagye, V. Andhalkar, W. Nabgan, S. Rtimi, and S. Contreras, “Advances in photo-catalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium: From fundamental concepts to materials design and technology challenges,” Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 50, p. 103301, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103301
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
วิธีการอ้างอิง
การอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารโลหะ, วัสดุ และแร่

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












