High temperature storage reliability of Cu pillar flip chip interconnects
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v36i1.2466คำสำคัญ:
High temperature storage, Reliability, Cu pillar bump, Intermetallic compoundบทคัดย่อ
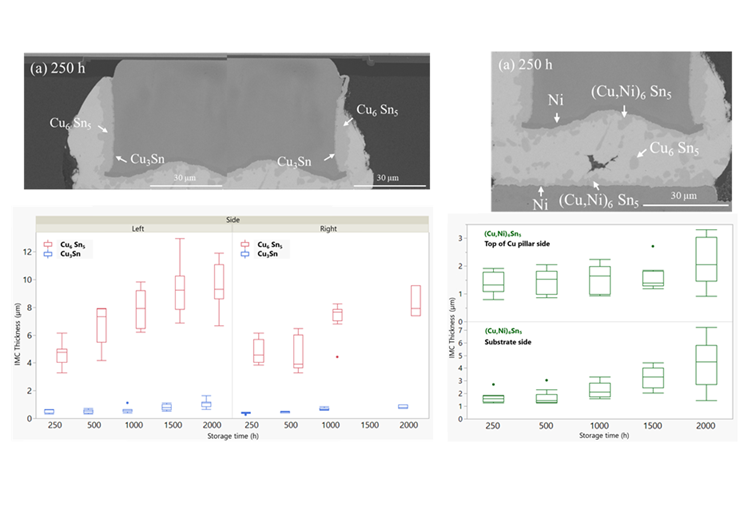
The Cu pillar flip chip is currently designed and used in the optic communication device that it has exhibited low reliability at high temperature. This paper aims to report the reliability of Cu pillar flip chip assembled on electronics board for a new optoelectronic product subjected to high temperature storage testing. The test was performed at 150℃ isothermal condition with the various storage times up to 2000 h. The aged samples were characterized with scanning acoustics microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Two types of intermetallic compounds (IMCs) were found at beside of the Cu pillar i.e. Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn. The Cu3Sn layer exhibits a thinner thickness (~0.62 mm at 1000 h) and a slower growth rate (~0.27 mm/1000 h) compared to the Cu6Sn5 layer (~7.96 mm and ~2.59 mm/1000 h). Cracks were commonly found at the IMC/Cu pillar sidewall interface that initiating at the solder edge on the pillar side with the smaller solder volume, then propagating along IMC/Cu interface. At the top of Cu pillar and substrate pad, which were coated by Ni layer, only (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 was found. The Ni layer influenced both the IMC type and growth rate. All IMCs exhibited increasing thickness with storage time. These findings provide important insights into the thermal reliability of a fine pitch Cu pillar solder interconnects in advanced electronic packaging.
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
K. Pongvittayapanu, A. Srisrual, and K. Fakpan, “Effect of thermal cycling and vibration on cracking in Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder bump,” Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 52, pp. 2372-2376, 2022.
J. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, Z. Chen, C. Zhou, X. Liu, and W.
Zhu, “The thermal cycling reliability of copper pillar solder bump in flip chip via thermal compression bonding,” Microelectronics Reliability, vol. 104, p. 113543, 2020.
R. Alberti, R. Enrici Vaion, A. Mervic, and S. Testa, “Metal fatigue in copper pillar Flip Chip BGA: A refined acceleration model for the aluminium pad cracking failure mechanism,” Microelectronics Reliability, vol. 55, pp. 1838–1842, 2015.
Q.-S. Zhu, Z.-F. Ding, X.-F. Wei, J.-dong Guo, and X.-J. Wang, “Effect of leveler on performance and reliability of copper pillar bumps in wafer electroplating under large current density,” Microelectronics Reliability, vol. 146, p. 115030, 2023.
S. Wang, J. Feng, W. Wang, P. Wu, J. Wen, D. Yang, Y. Huang, R. Tian, S. Wang, and Y. Tian, “Isothermal aging and electro-migration reliability of Cu pillar bumps interconnections in advanced packages monitored by in-situ dynamic resistance testing,” Journal of Materials Research and Technology, vol. 32, pp. 937-954, 2024.
X. Jing, W. Sun, L. Cao, P. He, and S. Zhang, “Phase tran-sformation, microstructural evolution and mechanical degradation of SnAg2.4/Cu solder joints at 160°C high-temperature storage test,” Materials Characterization, vol. 221, p. 114802, 2025.
U. S. Department of defense, “MIL-STD-883L 1005.11,” in Test Method Standard Environment Test Method for Microcircuits, 2019, pp. 27-36.
C. F. Coombs, Jr., Printed circuits handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008.
J. Libres, and J. C. Arroyo, “Investigation of bump crack and deformation on Pb-free flip chip packages,” Electronic Components and Technology Conference, pp. 1536-1540, 2010.
D. Kim, J. Park, J. Jang, H. Yang, K. Kim, and C. Oh, “Underfill material property dependence of lifetime and mechanical behavior of BGA package: EBSD and FEM investigations,” Microelectronics Reliability, vol. 150, p. 115113, 2023.
N. Ismail, W. Y. Wan Yusoff, A. Amat, N. A. A. Manaf, and N. Ahmad, “A review of extreme condition effects on solder joint reliability: Understanding failure mechanisms,” Defence Technology, vol. 41, pp. 134-158, 2024.
P. Jattakul, T. Madsa, P. Sunasuan, and N. Mookam, “Influence of cooling conditions on microstructure and mechanical property of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu lead-free solder,” Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 129-136, 2021.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
วิธีการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
บท
Categories
การอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 วารสารโลหะ, วัสดุ และแร่

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












