Effects of gum additives on nickel electroplating for enhancing steel corrosion resistance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v36i1.2334Keywords:
Electroplating, Nickel coating, Gum additives, Corrosion resistance, SteelAbstract
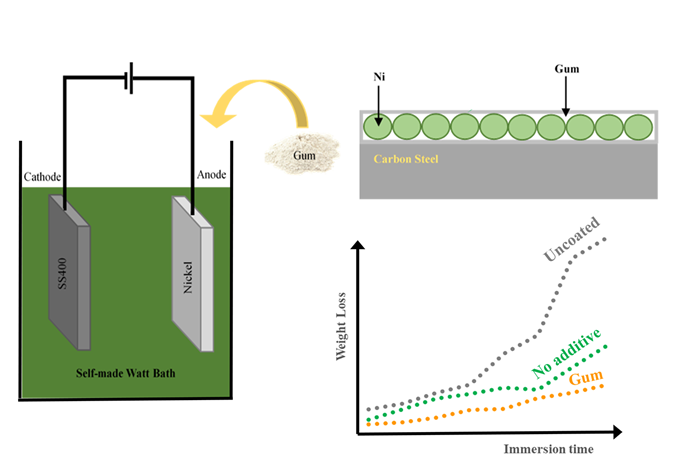
Low-carbon steels are widely used across various industries but have limited corrosion resistance, leading to safety hazards and a shortened service life. Nickel plating is a common method for enhancing steel corrosion resistance. The plating bath solution can be modified by adding additives to improve the properties of the coating. In this research, gum arabic, guar gum and gelatin were used as additives in a nickel electroplating bath. SS400 low-carbon steel, as a substrate, was plated with nickel from these different baths at 5 V for 25 min. Nickel coated with green additives showed higher hardness compared to those without additives, with the hardness of the coating using gum arabic measured at approximately 357 ± 6 HV. The morphology of the surface coating was characterized using SEM, which revealed that coating with gum arabic had a smooth surface, while those with gelatin and guar gum exhibited in an uneven or cracking surface, resulting in low hardness. The corrosion resistance was evaluated by immersing samples in a 3.5% NaCl solution. Nickel coatings with gum additives exhibited lower corrosion rates than those without. Among the additives, gum arabic demonstrated the best performance, producing the smoothest coating, the highest hardness, and the lowest corrosion rate.
Downloads
References
D. Dwivedi, K. Lepková, and T. Becker, “Carbon steel corrosion: A review of key surface properties and characterization methods,” RSC Advances, vol. 7, pp. 4580-4610, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA25094G
K. Bijapur, V. Molahalli, A. Shetty, A. Toghan, P. D. Padova, and G. Hegde, “Recent trends and progress in corrosion inhibitors and electrochemical evaluation,” Applied Sciences, vol. 13, p.10107, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810107
J. Liu, X. Fang, C. Zhu, X. Xing, G. Cui, and Z. Li, “Fabrication of superhydrophobic coatings for corrosion protection by electro-deposition: A comprehensive review,” Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, vol. 607, p.125498, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125498
D. Oloruntoba, O. Eghwubare, and L. Oluwole, “Effect of some process variables on nickel electroplating of low carbon steel,” Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies, vol. 18, pp. 79-94, 2011.
N. A. Badarulzaman, A. A. Mohamad, S. Puwadaria, and Z. A. Ahmad, “The evaluation of nickel deposit obtained via Watts electrolyte at ambient temperature,”Journal of Coatings Technology and Research, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 815-820, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-010-9271-4
U. S. Mohanty, B. C. Tripathy, P. Singh, A. Keshavarz1, and S. Iglauer, “Roles of organic and inorganic additives on the surface quality, morphology, and polarization behavior during nickel electrodeposition from various baths: A review,” Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, vol. 49, no. 9, pp. 847-870, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-019-01335-w
J. Wojciechowski, M. Baraniak, J. Pernak, and G. Lota, “Nickel coatings electrodeposited from watts type baths containing quaternary ammonium sulphate salts,” International Journal of Electrochemical Science, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 3350-3360, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.04.70
R. Riastuti, S.T. Siallagan, A. Rifki, F. Herdino, and C. Ramadini, “The effect of saccharin addition to nickel electroplating on the formation of nanocrystalline nickel deposits,” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 541, p. 012053, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/541/1/012053
E. Rudnik, and G. Chowaniec, “Effect of organic additives on electrodeposition of tin from acid sulfate solution,” Metallurgy and Foundry Engineering, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 41-52, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7494/mafe.2018.44.1.41
N. Sorour, W. Zhanga, E. Ghalia, and G. Houlachi, “A review of organic additives in zinc electrodeposition process (performance and evaluation),” Hydrometallurgy, vol. 171, pp. 320-332, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.06.004
T.-W. Zeng, and S.-C. Yen, “Effects of gelatin on electroplated copper through the use of a modified-hydrodynamic electro-plating test cell,” International Journal of Electrochemical Science, vol. 16, p. 210214, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.20964/2021.02.48
I. Kharmachi, L. Dhouibi, P. Berçot, M. Rezrazi, and B. Lakard, “Electrodeposition behavior, physicochemical properties and corrosion resistance of Ni–Co coating modified by gelatin additive,” Protection of Metals and Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 1059-1069, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117060132
W.Wu, “Effect of gelatin additive on microstructure and composition of electrodeposited rhenium–nickel alloys in aqueous solutions,” Applied Physics A, vol. 122, p. 1028, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0567-9
E. G. Temam, A. Elkhanssa, H. B. Temam, F. Kermiche, and H. Bentrah, “The influence of arabic gum on the catalytic properties of Ni-Mo alloy coatings to intensify hydrogen evolution reaction,” Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, vol. 64, no. 6, pp. 580-587, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/ACMM-10-2016-1722
S. T. Sudarsono, A. Aminur, I. Nurjannah, H. Hidayat, and R. Othman, “Effect of current density on hardness of low carbon steel electroplated by copper, nickel and copper-nickel,” IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 797, p. 012026, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/797/1/012026
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












