Use of oil palm frond waste to reinforce poly(lactic acid) based composites with the improvement of interfacial adhesion by alkali treatment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v32i1.1244Keywords:
Wood fiber composite, Oil palm frond, Poly(lactic acid), Alkali treatmentAbstract
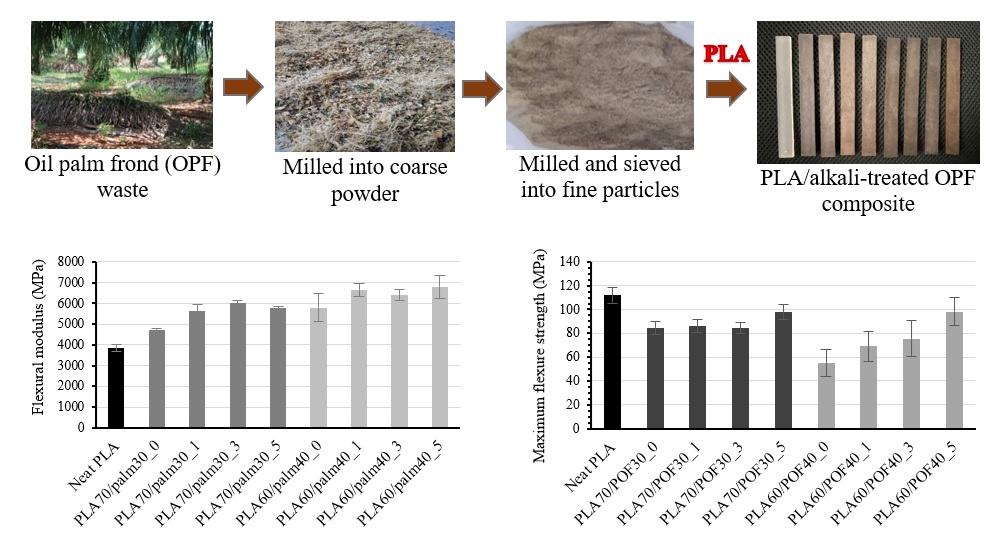
Oil palm frond waste was used as reinforcing fibers for biodegradable poly(lactic acid) or PLA in order to produce green composites that increased the value of agricultural waste. The alkali-treated oil palm frond (OPF) fibers of 30 wt% or 40 wt% were compounded with PLA and moulded into specimens. The alkali treatment was 0 wt%, 1 wt%, 3 wt%, and 5 wt% of the fibers for compatibility improvement with PLA matrix. It was found that the alkali-treated PLA/OPF composites adding 30 wt% and 40 wt% had the flexural modulus to be about 55% and 75% higher than those without the treatment, respectively. Tensile modulus of the composites was also increased. Nevertheless, the higher rigidity composites became more brittle as evident by the fracture toughness testing. The increase of total breaking energy confirmed the better interfacial adhesion between phases as shown in SEM micrographs. The glass transition temperature (Tg) of PLA matrix in the composites was shifted to lower temperature attributed to the thermal degradation of PLA during the melt compounding confirmed by the lower degradation temperature. Increasing the alkali concentration for surface treatment caused the Tg of PLA composites to be higher, supporting that the improvement of interfacial adhesion was achieved.
Downloads
References
I. Vroman, and L. Tighzert, "Biodegradable polymers," Materials, vol. 2, pp. 307-344, 2009.
A. Arbelaiz, U. Txueka, I. Mezo, and A. Orue, "Biocomposites based on poly(lactic acid) matrix and reinforced with lignocellulosic fibers: the effect of fiber type and matrix modification," Journal of Natural Fibers, 2020.
C. G. Silva, P. A. L. Campini, D. B. Rochaa, and D. S. Rosa, "The influence of treated eucalyptus microfibers on the properties of PLA biocomposites," Composites Science and Technology, vol. 179, pp. 54-62, 2019.
H. Peltola, K. Immonen, L. S. Johansson, J. Virkajärvi, and D. Sandquist, "Influence of pulp bleaching and compatibilizer selection on performance of pulp fiber reinforced PLA biocomposites," Journal of applied polymer science, vol. 136, no. 37, pp. 47955, 2019.
S. D. S. Kopparthy, and A. N. Netravali, "Review: Green composites for structural applications," Composites Part C, vol. 6, pp. 100169, 2021.
N. Laemsak, and M. Okuma, "Development of boards made from oil palm frond II: properties of binderless boards from steam-exploded fibers of oil palm frond," Journal of wood science, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 322-326, 2012.
A. E. Eladawi, and A. H. Rajpar, "Investigation of mechanical properties for reinforced polyester composites with palm fronds," Journal of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, vol. 8, pp. 74-84, 2020.
M. Russita, and Bahruddin, "Production of palm frond based wood plastic composite by using twin screw extruder," IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 345, pp. 012039, 2018.
D. Maheshwari, Composting for Sustainable Agriculture (Sustainable Development and Biodiversity). 2014.
W. Long, L. W. Lai, N. M. Rahim, E. F. Hashim, Z. Ya’cob, A. Idris, and J. Akhtar, "Study on composition, strutcural and property changes of oil palm frond biomass under different pretreatments," Cellulose Chemistry and Technology, vol. 50, pp. 951-959, 2016.
H. Chen, W. Zhang, X. Wang, H. Wang, Y. Wu, T. Zhong, and B. Fei, "Effect of alkali treatment on wettability and thermal stability of individual bamboo fibers," Journal of Wood Science, vol. 64, pp. 398-405, 2018.
E. Quero, A. J. Müller, F. Signori, M. B. Coltelli, and S. Bronco, "Isothermal cold-crystallization of PLA/PBAT blends with and without the addition of Acetyl Tributyl Citrate," Macro-molecular Journal, vol. 213, pp. 36-48, 2012.
S.-N. Sun, X.-F. Cao, H.-Y. Li, F. Xu, and R.-C. Sun, "Structural characterization of residual hemicelluloses from hydrothermal pretreated Eucalyptus fiber," International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 69, pp. 158-164, 2014.
P. Qu, Y. Goa, G. F. Wu, and L. P. Zhang, "Nanocomposite of poly(lactic acid) reinforced with cellulose nanofibrils," BioResources, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 1811-1823, 2010.
M. K. Mohamad Haafiz, Azman Hassan, Zainoha Zakaria, I. M. Inuwa, M. S. Islam, and M. Jawaid, "Properties of polylactic acid composites reinforced with oil palm biomass microcrystalline cellulose," Carbohydrate Polymers, vol. 98, no. 1, pp. 139-145, 2013.
N. A. Nordin, O. Sulaiman, R. Hashim, and M. H. M. Kassim, "Oil palm frond waste for the production of cellulose nanocrystals," Journal of Physical Science, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 115-126, 2017.
N. Hongsriphan, "Influence of chemical treatment and fiber content on color and properties of renewable wood composite using Ironwood saw dust," in The 2016 Pure and Applied Chemistry International Conference (PACCON 2016), BITEC, Bangkok, T. Vilaivan, Ed., 9-11 February 2016: The Chemical Society of Thailand under the Patronage of Professor Dr. HRH Princess Chulabhorn, pp. 1217-1222.
A. Leao, R. M. F. Teixeira, and P. Ferrão, "Production of reinforced composites with natural fibers for industrial applications – extrusion and injection WPC," Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, vol. 484, no. 1, pp. 157-166, 2008.
K. Al-Kaabi, A. Al-Khanbashi, and A. Hammami, "Natural fiber reinforced composites from Date palm fibers " in 11th European Conference on Composite Materials : from Nano-scale Interactions to Engineering Structures, Rhodes, Greece, C. Galiotis, Ed., May 31 - June 3, 2004.
C. Zhang, Q. Lan, T. Zhai, S. Nie, J. Luo, and W. Yan, "Melt crystallization behavior and crystalline morphology of poly-lactide/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends compatibilized by Lactide- Caprolactone copolymer," Polymers, vol. 10, pp. 1181, 2018.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












