Investigation on the tribological properties of Al\(_{2}\)O\(_{3}\)-TiC substrates in fixed abrasive lapping for data storage applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v36i1.2510คำสำคัญ:
AlTiC substrate, Fixed abrasive, Lapping material removal rate, Coefficient of friction, Surface finishบทคัดย่อ
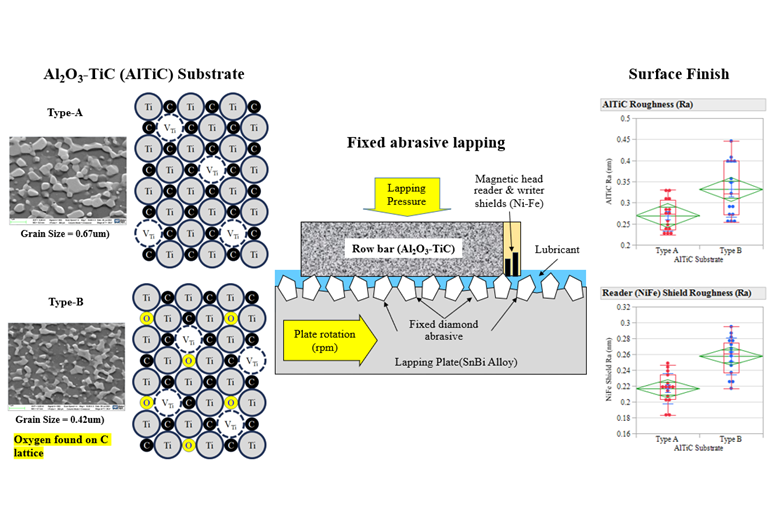
Alumina titanium-carbide (Al2O3-TiC) or simply AlTiC substrates were widely used in the magnetic recording industry for their superior mechanical and tribological properties. This study investigated the effect of AlTiC substrate crystal structure, chemical bonding and grain size in slider fix abrasive lapping tribology. Two types of AlTiC substrates, Type-A AlTiC and Type-B AlTiC equipped with an electro lapping guide (ELG), fully functional reader and writer devices were used in the study. The type-B lower material removal rate resulting to rougher surface finish was mainly due weakening caused by the titanium oxycarbide phase, which was the dominant factor, outweighing the minimal contribution from grain-boundary strengthening (Hall-Petch effect). Furthermore, the grain size investigated in this study was between 420 nm to 670 nm, making it far too large for the inverse Hall–Petch effect which involves softening at exceedingly small grain sizes typically below 100nm to be a relevant mechanism. The findings also highlight the importance of lapping parameters optimization to balance material removal rate (process productivity and efficiency) and surface finish (magnetic head reliability and areal density performance).
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
B. Liu, M. Zhang, S. Yu, L. Gonzaga, H.S. Hor, and J. Xu, “Femto slider: fabrication and evaluation,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 909-914, 2003.
L. Cheng, Z. Xie, G. Liu, W. Liu, and W. Xue, “Densification and mechanical properties of TiC by SPS-effects of holding time, sintering temperature and pressure condition,” Journal of the European Ceramic Society, vol. 32, no. 12, pp. 3399–3406, 2012.
M. Herrmann, and J. Räthel, “Hot pressing and hot isostatic pressing,” Elsevier eBooks, pp. 270–277, 2020
H. H. Gatzen, J. C. Maetzig, and M. K. Schwabe, “Precision machining of rigid disk head sliders,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 1843–1849, 1996.
H. H. Gatzen, and J. C. Maetzig: “Nanogrinding,” Precision Engineering-journal of The International Societies for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology, vol. 21, no. 2–3, pp. 134–139, 1997.
D.-E. Kim, K.-H. Chung, and K.-H. Cha, “Tribological design methods for minimum surface damage of HDD slider,” Tribology International, vol. 36, no. 4–6, pp. 467–473, 2003.
H. H. Gatzen, X. Ma, M. Scherge, M. S. Jhon, and C. L. Bauer, “Observations regarding the tribological properties of SiC and AlTiC sliders,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 3783–3785, 1996.
J. L. Sullivan, B. Shi, and S.O. Saied, “Microtribological studies of two-phase Al2O3–TiC ceramic at low contact pressure,” Tribology International, vol. 38, no. 11–12, pp. 987–994, 2005.
S. Jitphayomkun, P. Dechadilok, D. Tungasmita, S. Tungasmita, “Investigation on the tribological characteristics of lubricated Al2O3-TiC surface,” Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, vol. 29, no. 1 pp. 63–68, 2019.
H. Engqvist, and B. Uhrenius, “Determination of the average grain size of cemented carbides,” International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, vol. 21, no. 1–2, pp. 31–35, 2003
D. Adamovic, and F. Zivic, “Hardness and non-destructive testing (NDT) of ceramic matrix composites (CMCs),” Encyclopedia of Materials: Composites, pp. 183–201, 2021.
J. Gao, W. D. Luedtke, D. Gourdon, M. Ruths, J. N. Israelachvili, and U. Landman, “Frictional forces and Amontons’ law: From the molecular to the macroscopic scale,” The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, vol. 108, no. 11, pp. 3410–3425, 2004.
T. Deaconescu, and A. Deaconescu, “Developing an analytical model and computing tool for optimizing lapping operations of flat objects made of alloyed steels,” Materials, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 1343–1343, 2020.
K. F. Cai, D. S. McLachlan, N. Axen, and R. Manyatsa, “Preparation, microstructures and properties of Al2O3–TiC composites,” Ceramics International, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 217–222, 2002.
M. Madhan, and G. Prabhakaran, “Microwave versus conventional sintering: Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al2O3–SiC ceramic composites,” Boletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 14–22, 2018.
Z. Yin, C. Huang, B. Zou, H. Liu, H. Zhu, and J. Wang, “Study of the mechanical properties, strengthening and toughening mechanisms of Al2O3/TiC micro-nano-composite ceramic tool material,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, vol. 577, pp. 9–15, 2013.
Z. Cordero, B. E. Knight, and C. A. Schuh, “Six decades of the Hall–Petch effect – a survey of grain-size strengthening studies on pure metals,” International Materials Reviews, vol. 61, no. 8, pp. 495–512, 2016.
M. A. Meyers, A. Mishra, and D. J. Benson, “Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials,” Progress in Materials Science, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 427–556, 2006.
J. Schiøtz, F. D. Di Tolla, and K. W. Jacobsen, “Softening of nanocrystalline metals at very small grain sizes,” Nature, vol. 391, pp. 561–563, 1998.
S. Z. Chavoshi, and S. Xu, “Tension-compression asymmetry in plasticity of Nano twinned 3C-SiC nanocrystals,” Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 124, no. 9, 2018.
Q. An, and W. A. Goddard, “Nanotwins soften boron-rich boron carbide (B13C2),” Applied Physics Letters, vol. 110, no. 11, 2017
S. Z. Chavoshi, and S. Xu, “Twinning effects in the single/ nanocrystalline cubic silicon carbide subjected to nano-indentation loading,” Materialia, vol. 3, pp. 304–325, 2018
M. Ivanovskaya, E. Ovodok, D. Kotsikau, I. Azarko, M. Micusik, M. Omastova, and V. Golovanov, “Structural transformation and nature of defects in titanium carbide treated in different redox atmospheres,” RSC Advances, vol. 10, no. 43, pp. 25602–25608, 2020.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
วิธีการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
บท
Categories
การอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 วารสารโลหะ, วัสดุ และแร่

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












