Recycling of iron oxide waste by carbothermic reduction to utilize in FDM 3D printing materials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v33i2.1584คำสำคัญ:
Reduced iron, Waste, ABS composite, 3D printing, Filamentบทคัดย่อ
Iron oxide scale generally forms on low-carbon steel surfaces during the hot rolling processes and
produces as solid waste more than 100 thousand tons per year. The utilization of the iron oxide scale
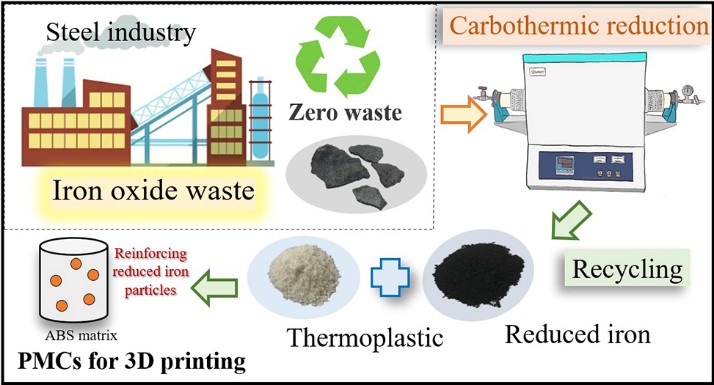
is one possible way to reduce the production cost for steel plants and promote environmental protection. Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrol-Copolymer (ABS) is widely used as engineering plastic for automotive parts because of its high strength and wear resistance. The recycling of iron oxide waste as reinforcement particles for enhancing the tensile strength of ABS composite was studied. The iron oxides were recycled by carbon powder at a high temperature between 1150℃ to 1350℃ up to 120 min. After the reduction process, the reduced iron from an optimal condition with the iron-rich fraction was ground to powder. Afterward, the 0.3 vol% to 1.3 vol% powders were mixed with ABS polymer powder and formed as composite filaments for additive manufacturing (FDM 3D printing). The tensile strength of pure ABS filament increased to 37.16 ± 2.37 MPa when added recycled iron powders. The regular distribution and 13.68 ± 9.78 µm of recycled-iron particle sizes on the ABS matrix were investigated and correlated to the mechanical properties.
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
V. B. Ginzburg, Flat-Rolled Steel Processes (Advanced Technologies), CRC Press, 2009.
B. T. Hang and T. T. Anh, “Controlled synthesis of various Fe2O3 morphologies as energy storage materials,” Sci Rep, vol. 11, pp. 5185, 2021.
A. Babich, D. Senk, and H.W. Gudenau, Ironmaking, Stahleisen, Düsseldorf, 2016.
O. Benchiheub, S. Mechachti, S. Serrai, and M. G. Khalifa. “Elaboration of iron powder
from Mill scale,” J. Mater. Environ. Sci., vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 267-276, 2010.
M. C. Bagatini, V. Zymla, E. Osório, and A.C.F. Vilela, “Characterization and Reduction Behavior of Mill Scale,” ISIJ International, vol. 51, issue 7, pp. 1072–1079, 2011.
K. S. Sista and S. Dwarapudi, “Iron Powders from Steel Industry by-products,” ISIJ International, vol. 58, no. 6, 2018.
S. N. Nagesh, C. Siddaraju, S. V. Prakash, and M. R. Ramesh, “Characterization of brake pads by variation in composition of friction materials,” Procedia Materials Science, vol. 5, pp. 295-302, 2014.
C. Suwanpreecha, S. Songkuea, S. Linjee, S. Muengto, M. Bumrungpon, and A. Manonukul, “Tensile and axial fatigue properties of AISI 316L stainless steel fabricated by materials extrusion additive manufacturing”, Materials Today Communications, vol. 35, 2023.
J. Surisaeng, W. Kanabenja, N. Passornraprasit, and C. Aumnate, “Polyhydroxybutyrate/polylactic acid blends: An alternative feedstock for 3D printed bone scaffold model,” J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., vol. 2175, 2022.
B. Thavornyutikarn, P. Tesavibul, K. Sitthiseripratip, N. Chatarapanich, B. Feltis, P. F. Wright, and T. W. Turney, “Effect of partial pre-sintering on structural and mechanical properties of scaffolds,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C, vol. 75, pp. 1281-1288, 2017.
K. Sakunphokesup, P. Kongkrengkri, A. Pongwisuthiruchte, C. Aumnate, and P. Potiyaraj, “Graphene-enhanced ABS for FDM 3D printing: effects of masterbatch preparation techniques,” IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 600, 2019.
P. L. López, Mechanical characterization of composite materials: fracture energies, Madrid: Universidad Carlos III de Madrid., Inc., 2018.
K. A. Hamzah, C. K. Yeoh, M. M. Noor, P. L. Teh, Y. Y. Aw, S. A. Sazali, and W. M. A. W. Ibrahim, “Mechanical properties and thermal and electrical conductivity of 3D printed ABS-copper ferrite composites via 3D printing technique,” Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, vol. 35, 2019.
S.S. Aqzna, C.K. Yeoh, M.S. Idris, P.L. Teh, K.A. bin Hamzah, Y. Y. Aw, and T. N. Atqah, “Effect of different filler content of ABS-zinc ferrite composites on mechanical, electrical, and thermal conductivity by using 3D printing,” Journal of Vinyl and Additive Technology, vol.24, issue S1, pp. E217-E229, 2018.
F. Ning, W. Cong, J. Qiu, J. Wei, and S. Wang, “Additive manufacturing of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites using fused deposition modeling,” Composites Part B: Engineering, vol. 80, pp. 369-378, 2015.
K. S. Boparai, and R. Singh, and H. Singh, “Wear behavior of FDM parts fabricated by composite material feed stock filament,” Rapid Prototyping Journal, vol. 22, issue 2, pp. 350-357, 2016.
B. B. Difallah, M. Kharrat, M. Dammak, and G. Monteil, “Mechanical and tribological response of ABS polymer matrix filled with graphite powder,” Materials & Design, vol.43, pp. 782-787, 2012.
M. A. Ryder, D. A. Lados, G. S. Iannacchione, and A. M. Peterson, “Fabrication and properties of novel polymer-metal composites using fused deposition modeling,” Composites Science and Technology, vol. 158, pp.43-50, 2018.
S. Hwang, E.I. Reyes, Ks. Moon, R. C. Rumpf, and N. S. Kim, “Thermo-mechanical Characterization of Metal/Polymer Composite Filaments and Printing Parameter Study for Fused Deposition Modeling in the 3D Printing Process.” J. Electron. Mater., vol. 44, pp. 771–777, 2015.
N. Chawla, Metal Metrix Composite. United States of America: Springer Science Business Media, Inc., 2006.
M. Kutz, " Chapter 10 Composite Materials " in Handbook of Mechanical Engineers, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2015, pp. 401-420.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
วิธีการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
บท
การอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 วารสารโลหะ, วัสดุ และแร่

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












