Possibility of using boric acid and glutinous rice flour as additive for producing silicon carbide ceramic via pressureless solid-state sintering
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v34i1.1939Keywords:
silicon carbide, ceramics, glutinous rice flour, boric acid, pressureless solid-state sinteringAbstract
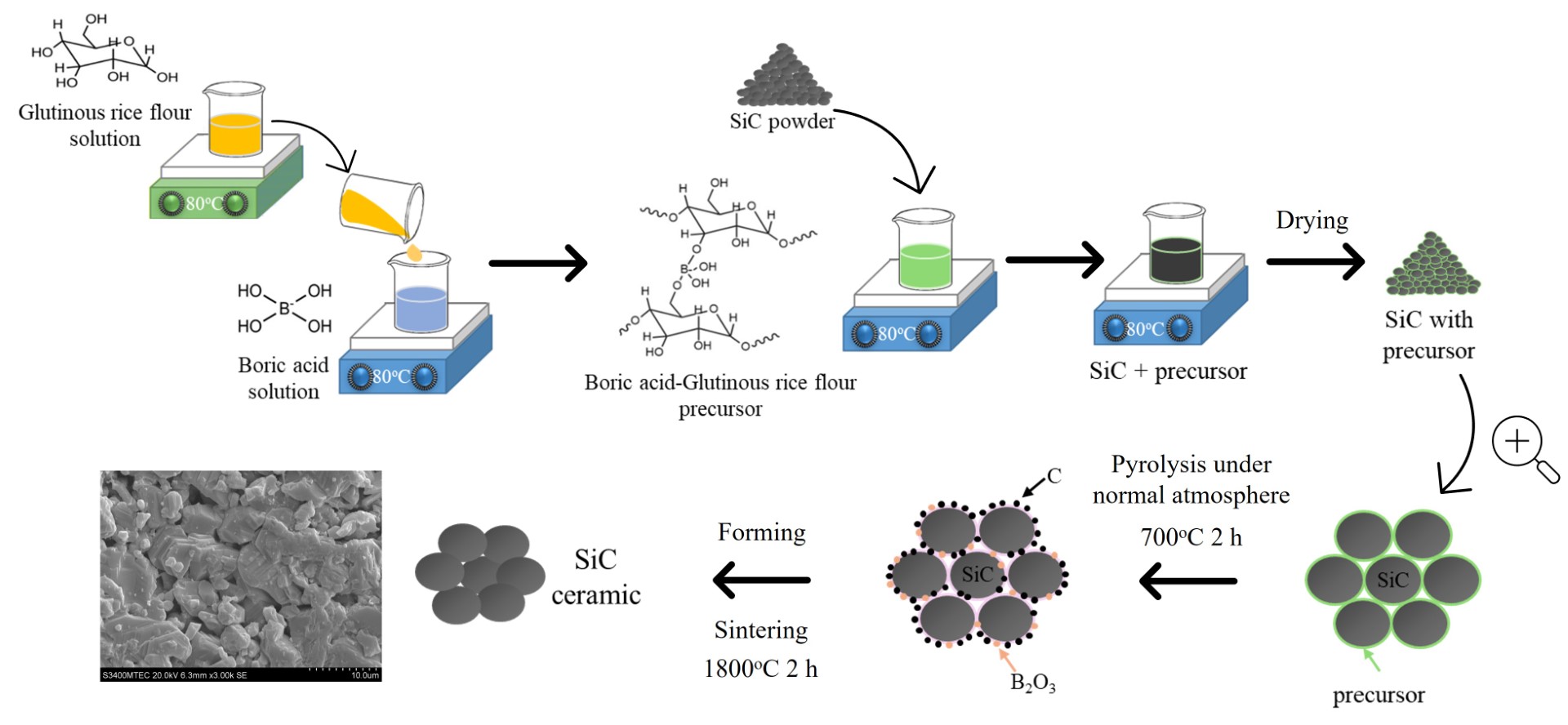
This research aimed to investigate the possibility of using the mixture of boric acid and glutinous rice flour as a cost-efficient alternative additive for producing silicon carbide (SiC) ceramic sintered at 1800℃ via pressureless solid-state sintering. The results indicated that the addition of boric acid- glutinous rice flour mixture (10 wt%) in an appropriate ratio (0.5 by molar ratio) into the SiC mixture (90 wt%) enhanced the densification and flexural strength of sintered SiC samples. However, increasing boric acid/glutinous rice flour ratio reduces density and flexural strength. The 5.45 wt% carbon content was sufficient to remove the oxide layer of the SiC surface and improve the properties of SiC ceramic. In summary, the boric acid-glutinous rice flour mixture has a high potential to be used as an additive for producing dense and porous SiC ceramics via pressureless solid-state sintering.
Downloads
References
G. Magnani, A. Brentari, E. Burresi, and G. Raiteri, "Pressureless sintered silicon carbide with enhanced mechanical properties obtained by the two-step sintering method," Ceramics International, vol. 40, pp. 1759-1763, 2014.
Z. Aygüzer Yaşar, V. A. DeLucca, and R. A. Haber, "Influence of oxygen content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SPS SiC," Ceramics International, vol. 44, pp. 23248-23253, 2018.
Q. W. Huang, and L. H. Zhu, "High-temperature strength and toughness behaviors for reaction-bonded SiC ceramics below 1400°C," Materials Letters, vol. 59, pp. 1732-1735, 2005.
M. khodaei, O. yaghobizadeh, S. H. Naghavi Alhosseini, S. esmaeeli, and S. R. Mousavi, "The effect of oxide, carbide, nitride and boride additives on properties of pressureless sintered SiC: A review, " Journal of the European Ceramic Society, vol. 39, pp. 2215-2231, 2019.
Z. Aygüzer Yaşar, V. A. DeLucca, and R. A. Haber, "Effect of boron carbide additive and sintering temperature - Dwelling time on silicon carbide properties," Ceramics International, vol. 47, pp. 7177-7182, 2021.
G. D. Kim, Y. W. Kim, S. M. Yong, and W. K. Jung, "Improving specific stiffness of silicon carbide ceramics by adding boron carbide," Journal of the European Ceramic Society, vol. 42, pp. 6827-6835, 2022.
A. Szkliniarz and W. Szkliniarz, "Effect of carbon content on the microstructure and properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy," Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, vol. 65, pp. 1197-1204, 2020.
S. Prochazka and R. M. Scanlan, "Effect of boron and carbon on sintering of SiC," Journal of the American Ceramic Society, vol. 58, pp. 72-72, 1975.
R. Malik, and Y. W. Kim, "Pressureless solid-state sintering of SiC ceramics with BN and C additives," Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, vol. 9, pp. 1165-1172, 2021.
D. C. Jana, P. Barick, and B. P. Saha, "Effect of sintering temperature on density and mechanical properties of solid-state sintered silicon carbide ceramics and evaluation of failure origin," Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, vol. 27, pp. 2960-2966, 2018.
M. Liu, Y. Yang, Y. Wei, Y. Li, H. Zhang, X. Liu, and Z. Huang, "Preparation of dense and high-purity SiC ceramics by pressureless solid-state-sintering," Ceramics International, vol. 45, pp. 19771-19776, 2019.
G. Liu, Z. Gu, Y. Hong, L. Cheng, and C. Li, "Electrospun starch nanofibers: Recent advances, challenges, and strategies for potential pharmaceutical applications," Journal of Controlled Release, vol. 252, pp. 95-107, 2017.
P. Jaiturong, B. Sirithunyalug, S. Eitsayeam, C. Asawahame, P. Tipduangta, and J. Sirithunyalug, "Preparation of glutinous rice starch/polyvinyl alcohol copolymer electrospun fibers for using as a drug delivery carrier," Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol. 13, pp. 239-247, 2018.
K. Dateraksa and S. Sinchai, "Phase formation of boron carbide powder synthesized from glutinous rice flour," Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, vol. 29, pp. 48-53, 2019.
R. McCuiston, S. Ngernbamrung, K. Dateraksa, K. Sujirote, J. Wannasin, and T. Sungkapun, "Fabrication of high-volume fraction SiCp/Al metal matrix composites," Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, vol. 32, pp. 71-80, 2011.
Y. Zhou, W. Sha, Y. Liu, Y. Lyu, and Y. Huang, "Influence of carbon source on microstructural and mechanical properties of high-performance reaction-bonded silicon carbide," Materials, vol. 15, pp. 5250, 2022.
Z. A. Yaşar, and R. A. Haber, "Effect of carbon addition and mixture method on the microstructure and mechanical properties of silicon carbide," Materials, vol. 13, p. 3768, 2020.
M. S. Datta, A. K. Bandyopadhyay, and B. Chaudhuri, "Sintering of nano crystalline α silicon carbide by doping with boron carbide," Bulletin of Materials Science, vol. 25, pp. 181-189, 2002.
A. Maître, A. V. Put, J. P. Laval, S. Valette, and G. Trolliard, "Role of boron on the spark plasma sintering of an α-SiC powder," Journal of the European Ceramic Society, vol. 28, pp. 1881-1890, 2008.
L. Stobierski, and A. Gubernat, "Sintering of silicon carbide II. Effect of boron," Ceramics International, vol. 29, pp. 355-361, 2003.
H. Skarpeid, "The effect of carbon and boron carbide additions in pressure assisted sintered silicon carbide," Master’s thesis, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2017.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












