Influence of annealing times for W films on the structure and electrochromic properties of anodized WO\(_{3}\) films
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v34i2.1969Keywords:
WO3, annealing, sputtering, anodization, electrochromic propertiesAbstract
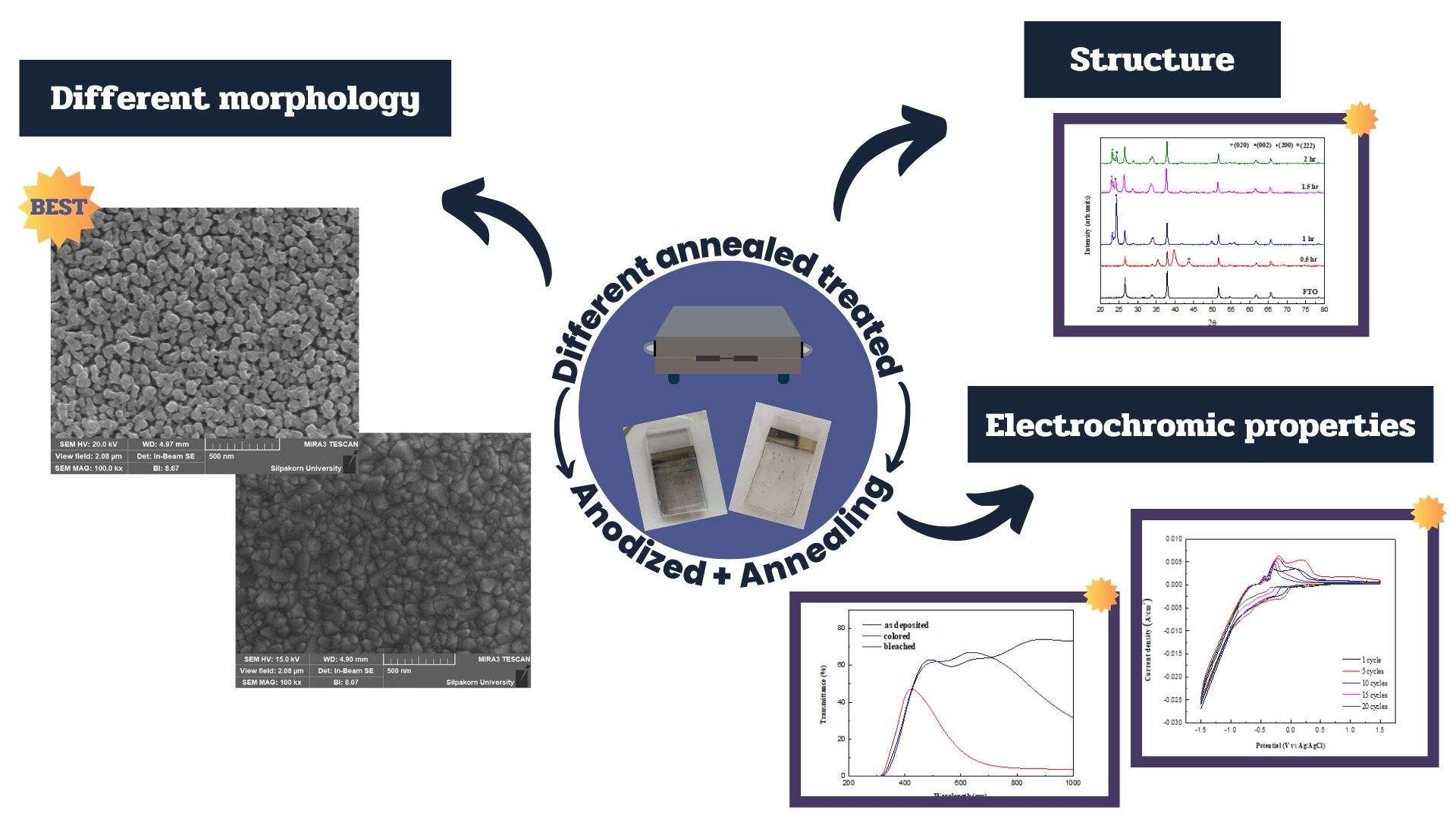
WO3 films were prepared from annealed W films by anodization and annealing at 450℃ for 1 h. The sputtered W films were annealed before anodization at different times for 0.5 h to 2 h, followed by immediate removal from the furnace (quenching) or slow cooling (cool-down). The WO3 films exhibited a different preferred orientation between the (200) and (222) planes. The morphological structure of the WO3 films depended on the annealing time and cooling features of the W films. The WO3 films for the cool-down condition had smaller grains and more pores than the quenching condition. The WO3 films prepared from annealed W for 1.5 h with cool-down showed maximum transmittance change of 48.20% with the diffusion coefficient of 3.533 x 10-7 cm2∙s‒1. The quenching condition can be improved durability of WO3 films. Therefore, annealing time and cooling conditions can be used to design film properties that are suitable for the electrochromic application.
Downloads
References
C. Aiempanakit, A. Chanachai, N. Kanchal, M. Aiempanakit, and K. Aiempanakit, "Electrochromic property of tungsten trioxide films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering with oblique angle deposition and thermal oxidation," Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, vol. 31, pp. 123-128, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v31i2.1084
D. Zhou, and L. Yang, "Enhanced electrochromic properties of nanocrystalline molybdenum oxide f ilms modified by dopamine," Coatings, vol. 13, pp. 1292, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13071292
B. Zhang, C. Xu, G. Xu, S. Tan, and J. Zhang, "Amorphous titanium dioxide film with improved electrochromism in nearinfrared region," Optical Materials, vol. 89, pp. 191-219, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2019.01.034
W. Zhao, J.Wang, B. Tam, P. Pei, F. Li, A. Xie, and W. Cheng, "Macroporous vanadium oxide ion storage films enable fast switching speed and high cycling stability of electrochromic devices," Applied Materials & Interfaces, vol. 14, pp. 30021-30028, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c05492
W. Thongjoon, I. Chuasontia, K. Aiempanakit, and C. Aiempanakit, "Morphology and electrochromic property of chemical bath deposited NiO films at different NiSO4 concentration," Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, vol. 32, pp. 87-92, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.55713/jmmm.v32i4.1534
V. Madhavi, P. Kondaiah, O.M. Hussain, and S. Uthanna, "Structural, optical and electrochromic properties of RF magnetron sputtered WO3 thin films," Physica B, vol. 454, pp. 141-147, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.07.029
X. Li, Z. Li, W. He, H. Chen, X. Tang, Y. Chen, and Y. Chen, "Enhanced electrochromic properties of nanostructured WO3 film by combination of chemical and physical methods," Coatings, vol. 11, pp. 959, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11080959
C. Y. Ng, K. A. Razak, and Z. Lockman, "Effect of annealing temperature on anodized nanoporous WO3," Journal Porous Mater, vol. 22, pp. 537–544, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-9924-x
C. Aiempanakita, R. Momkhunthoda, and K. Aiempanakit, "Electrochromism in nanoporous tungsten trioxide films prepared through anodization and thermal oxidation," Integrated Ferroelectrics, vol. 222, pp. 84-92, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2021.1961518
Y. Liu, N. Jiang, Y. Liu, D. Cui, C.F. Yu, H. Liu, and Z. Li, "Effect of laser power density on the electrochromic properties of WO3 films obtained by pulsed laser deposition," Ceramics International, vol. 47, pp. 22416-22423, 2021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.251
Y. Shi, M. Sun, W. Chen, Y. Zhang, X. Shu, Y. Qin, X. Zhang, H. Shen, and Y. Wu, "Rational construction of porous amorphous WO3 nanostructures with high electrochromic energy storage performance: Effect of temperature," Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, vol. 549, p. 120337, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120337
J. Zhang, X. L. Wang, X. H. Xia, C. D. Gu, Z. J. Zhao, and J. P. Tu, "Enhanced electrochromic performance of macroporous WO3 films formed by anodic oxidation of DC-sputtered tungsten layers," Electrochimica Acta, vol. 55, pp. 6953-6958, 2010.
P. V. Ashrit, "Dry lithiation study of nanocrystalline, poly-crystalline and amorphous tungsten trioxide thin-film," Thin Solid Films, vol. 385, pp. 81-88, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(00)01895-2
Y. Zhang, X. Liang, T. Jiang, H. Liu, Y. Fu, D. Zhang, and Z. Geng, "Amorphous/crystalline WO3 dual phase laminated films: Fabrication, characterization and evaluation of their electrochromic performance for smart window applications," Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, vol. 244, p. 111820, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2022.111820
K. K. Purushothaman, G. Muralidharan, and S. Vijayakumar, "Sol-Gel coated WO3 thin films based complementary electro-chromic smart windows," Materials Letters, vol. 296, p. 129881, 2021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129881
R.M. Fernandez-Domene, G. Rosello-Marquez, R. Sanchez-Tovar, M. Cifre-Herrando, and J. GarcíaAnton, "Synthesis of WO3 nanorods through anodization in the presence of citric acid: Formation mechanism, properties and photoelectrocatalytic performance," Surface & Coatings Technology, vol. 422, p. 127489, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127489
J. Zhang, X.L. Wang, X.H. Xia, C.D. Gu, Z.J. Zhao, J.P. Tu, "Enhanced electrochromic performance of macroporous WO3 films formed by anodic oxidation of DC-sputtered tungsten layers," Electrochimica Acta, vol. 55, pp. 6953-6958, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.06.082
T. Zhang, M. Paulose, R. Neupane, L. A. Schaffer, D. B. Rana, J. Su, L. Guo, and O. K. Varghese, "Nanoporous WO3 films synthesized by tuning anodization conditions for photoelectro-chemical water oxidation," Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, vol. 209, p. 110472, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110472
B. W. Au, A. Tamang, D. Knipp, and K. Y. Chan, "Post-annealing effect on the electrochromic properties of WO3 films," Optical Materials, vol. 108, pp. 110426, 2020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110426
K. Kalantar-zadeha, A. Z. Sadek, H. Zheng, V. Bansal, S. K. Bhargava, W. Wlodarski, J. Zhu, L. Yu, and Z. Hu, "Nano-structured WO3 films using high temperature anodization," Sensors and Actuators B, vol. 142, pp. 230–235, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.08.014
F. A. Akgul, G. Akgul, N. Yildirim, H. E. Unalan, and R. Turan "Influence of thermal annealing on microstructural, morphological, optical properties and surface electronic structure of copper oxide thin films," Materials Chemistry and Physics, vol. 147, pp. 987-995, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.06.047
K. Pandurangarao, V. C. Babu, and V. R. Kumar, "Synthesis and characterization of Ti-WO3 films for electrochromic applications," Optical Materials, vol. 136, p. 113381, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.113381
P. J. Boruah, R. R. Khanikar, and H. Bailung, "Synthesis and characterization of oxygen vacancy induced narrow bandgap tungsten oxide (WO3−x) nanoparticles by plasma discharge in liquid and its photocatalytic activity," Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, vol. 40, pp. 1019-1036, 2020.–1036, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-020-10073-3
H. Kim, D. Choi, K. Kim, W. Chu, D. Chun, and C. S. Lee, "Effect of particle size and amorphous phase on the electro-chromic properties of kinetically deposited WO3 films," Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, vol. 177, pp. 44-50, 2018.
K. V. Madhuri, and M. B. Babu, "Influence of substrate temperature on growth and electrochromic properties of WO3 thin films," Optik, vol. 174, pp. 470-480, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.08.028
C. Aiempanakit, M. Aiempanakit, W. Thongjoon, S. Pudwat, and K. Aiempanakit, "Characterization and electrochromic properties of multi-morphology NiO films prepared by CBD and DC Techniques," Optik, vol. 287, pp. 171131, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2023.171131
H. Kim, D. Choi, K. Kim, W. Chu, D. Chun, and C. S. Lee, "Effect of particle size and amorphous phase on the electro-chromic properties of kinetically deposited WO3 films," Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, vol. 177, pp. 44-50, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2017.06.010
Y. Zhao, X. Zhang, X. Chen, W. Li, L. Wang, F. Ren, J. Zhao, F. Endres, and Y. Li, "Preparation of WO3 films with controllable crystallinity for improved near-infrared electrochromic performances," ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng, vol. 8, pp. 11658-11666, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c03141
K. K. Purushothaman, ans G. Muralidharan, "The effect of annealing temperature on the electrochromic properties of nanostructured NiO films," Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, vol. 93, pp. 1195-1201, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2008.12.029
D. Choi, M. Son, T. Im, S. Ahn, and C. S. Lee, "Micro-structure control of NiO-based ion storage layer with various sized NiO particles to evaluate the electrochromic performance," Materials Chemistry and Physics, vol. 249, p. 123121, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123121
Z. Xia, H. Wan, Y. Su, P. Tang, M. Dai, H. Lin, Z. Zhang, and Q. Shi, "Enhanced electrochromic properties by improvement of crystallinity for sputtered WO3 film," Coatings, vol. 10, p. 577, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060577
M. Arslan, Y.E. Firat, S.R. Tokgoz¨, and A. Peksoz, "Fast electrochromic response and high coloration efficiency of Al-doped WO3 thin films for smart window applications," Ceramics International, vol. 47, pp. 32570-32578, 2021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.152
S. B. Patil, and S. B. Sadale, "Size-dependent electrochemical kinetics of nano-granular WO3 thin films," Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, vol. 245, pp. 111849, 2022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2022.111849
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.












